When it comes to healthcare, some countries consistently stand out for the quality of their medical professionals and systems. While “best” can be a subjective term, these nations often lead the way in patient outcomes, advanced medical technology, and the overall well-being of their populations.
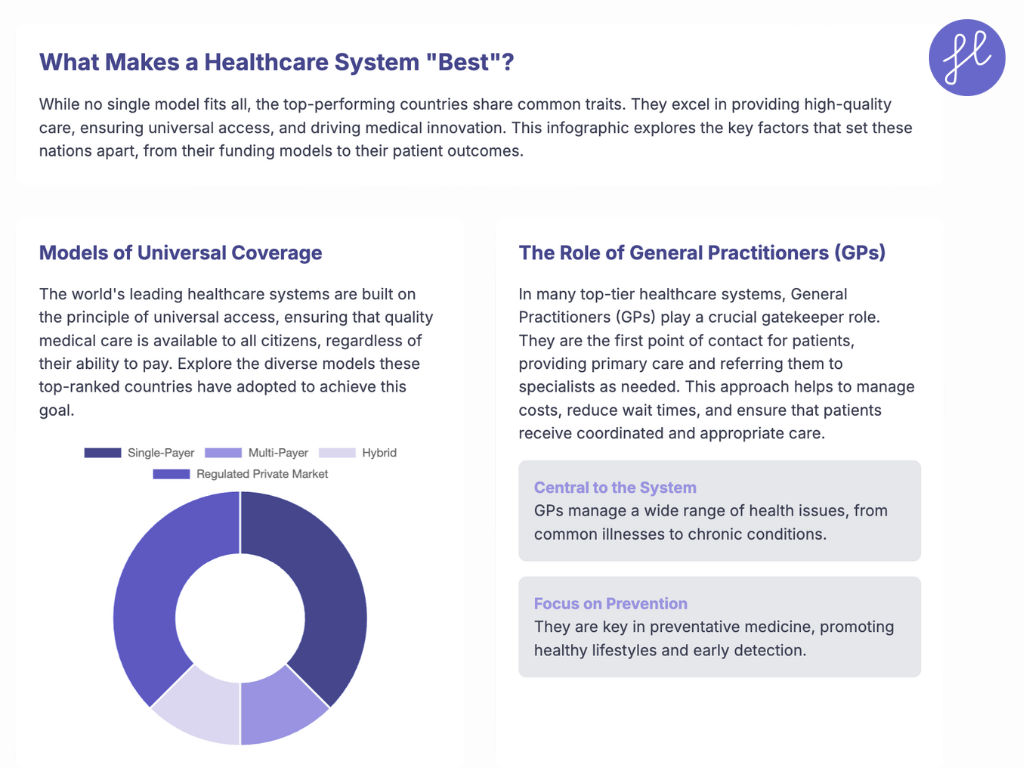
Here is a detailed look at the countries known for having some of the best doctors in the world.
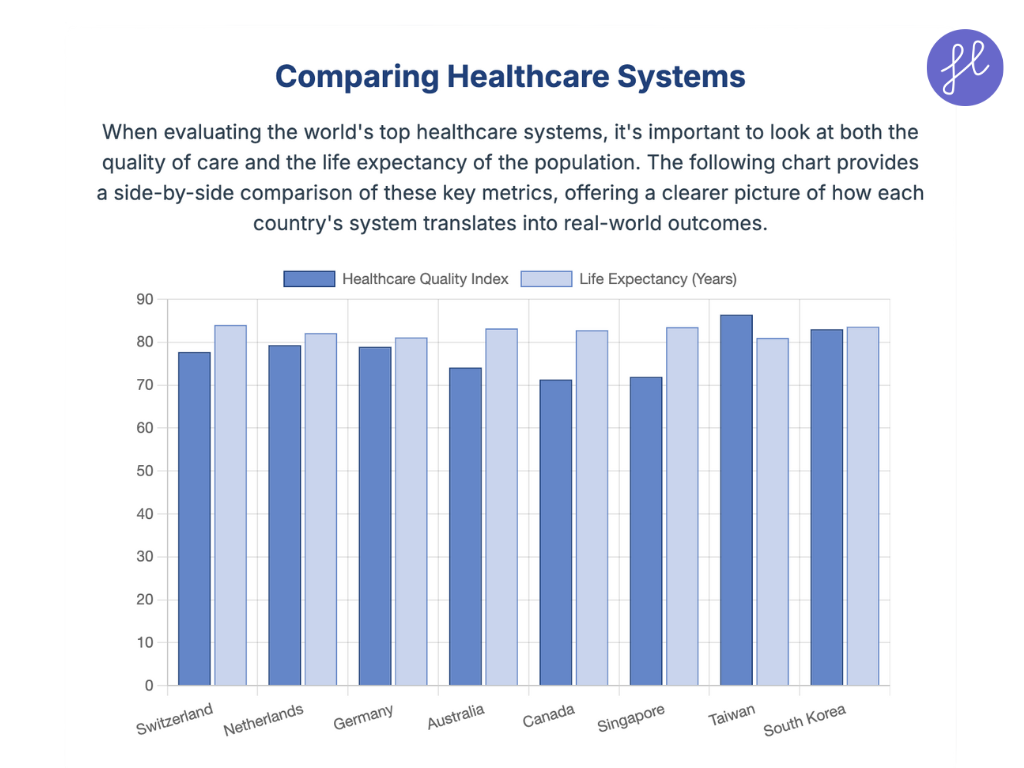
1. Switzerland

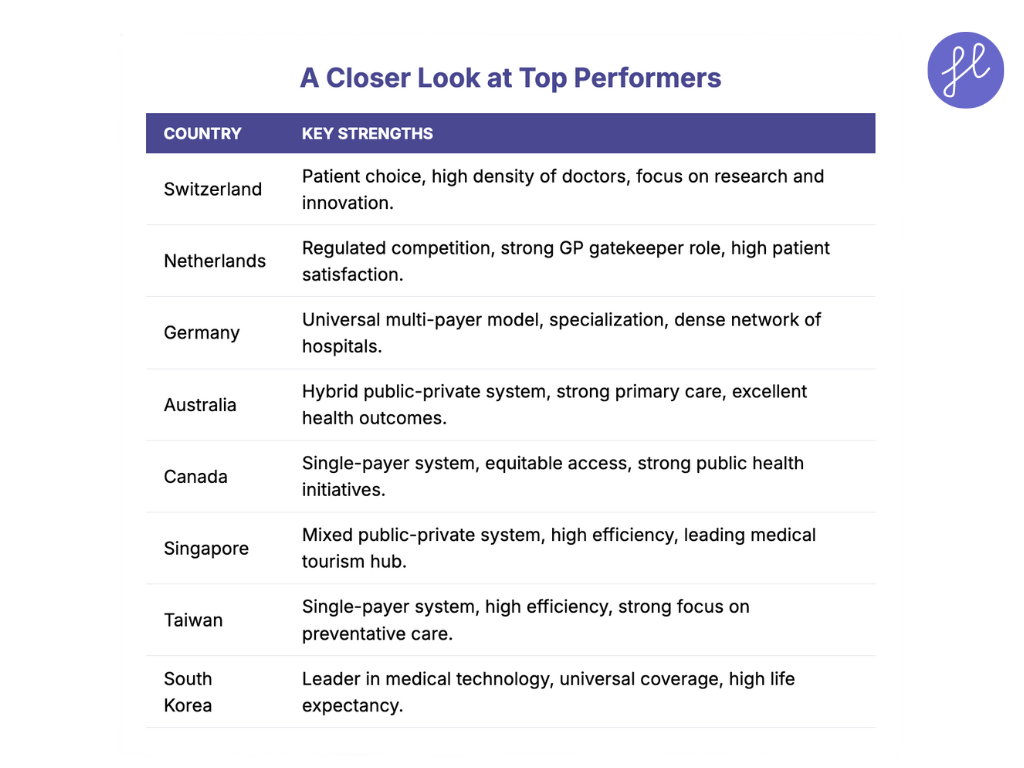
Switzerland’s healthcare system is renowned for its high-quality, universal coverage, and its focus on patient choice. The system is mandatory for all residents and operates on a private insurance model, where individuals purchase basic health insurance from one of about 60 private, non-profit insurers.
The government provides subsidies for low-income residents to ensure affordability. This system fosters competition among insurers, which drives efficiency and responsiveness to patient needs. Swiss doctors are among the best trained in the world, with high densities of medical staff and nurses.
The system’s emphasis on research and innovation means patients have access to cutting-edge treatments and advanced medical technologies.
2. The Netherlands

The Netherlands has one of the world’s most highly-regarded healthcare systems, often ranked at the top for efficiency and patient satisfaction. Its system, based on “regulated competition,” requires all citizens to purchase a basic health insurance package from a private insurer. Insurers must accept all applicants, regardless of age or health status.
The government regulates the basic package and subsidizes premiums for low-income citizens, ensuring universal access. The Dutch system is notable for its strong gatekeeper role of general practitioners (GPs), who act as the first point of contact and referrals to specialists.
Doctors are well-trained and focus on preventative medicine, contributing to the country’s impressive health outcomes.
3. Germany

Germany’s healthcare system, the oldest in Europe, is a universal multi-payer model that offers comprehensive coverage. It is a dual system, with most of the population (approximately 90%) covered by Statutory Health Insurance (SHI), also known as “sickness funds.” At the same time, high-income earners and civil servants can opt for private insurance. Contributions to the SHI are income-based and shared by employers and employees, making it highly equitable.
Germany’s doctors and hospitals are considered world-class, with a strong emphasis on specialization and medical research. Patients have the freedom to choose their doctors and specialists, and the well-funded system ensures access to advanced technologies and services.
The decentralized governance of the system, with states having significant authority, contributes to a dense network of hospitals and clinics, ensuring accessibility for all.
Check out What Germany is a Premier Destination for Medical Specialization
4. Australia

Australia operates a hybrid healthcare system with a mix of public and private services. The cornerstone is Medicare, a universal, single-payer public health insurance system funded by a progressive tax levy. Medicare provides free treatment in public hospitals and subsidized access to primary care from GPs and some specialists.
This system ensures that all citizens and permanent residents have access to essential healthcare. In addition, many Australians opt for private health insurance to gain more choice, such as shorter waiting times for elective surgeries, their preferred doctor, and private hospital rooms.
Australian doctors are highly trained, and their public health focus, primarily through the strong emphasis on primary care, contributes to excellent health outcomes and a high life expectancy.
5. Canada

Canada’s publicly funded, single-payer healthcare system, colloquially known as Medicare, is a core part of its national identity. It provides universal coverage for all citizens and permanent residents for “medically necessary” hospital and physician services. Individual provinces and territories administer the system, but it must adhere to the national standards set by the Canada Health Act.
Canadian doctors are highly respected and well-trained. While the system is celebrated for ensuring that no one is denied care based on their ability to pay, it can face challenges with longer wait times for some non-emergency procedures.
The focus is on providing all citizens with equitable access to essential services, regardless of income or location, which is a significant strength of the system.
6. Singapore

Singapore’s healthcare system is a fascinating model of a mixed public-private system that balances government regulation with market-based elements. The system is known for its efficiency and excellent patient outcomes.
It is funded through a combination of a national health savings scheme (Medisave), national health insurance (MediShield Life), government subsidies, and out-of-pocket payments.
This system encourages personal responsibility for health costs while ensuring that no one is left behind. Doctors in Singapore are highly skilled, and the country has invested heavily in medical infrastructure and technology, making it a leading medical tourism destination.
7. Taiwan
Taiwan’s healthcare system is frequently hailed as one of the best in the world, often topping international indexes. This is mainly due to its efficient, single-payer National Health Insurance (NHI) system, which was implemented in 1995. The system provides universal coverage to over 99% of the population, offering a high level of patient choice and accessibility.
Patients in Taiwan have quick access to specialists without needing a referral from a general practitioner. The use of a single, comprehensive electronic medical record system for the entire population streamlines patient care and reduces administrative costs.
Taiwan’s doctors are highly trained, and the country’s medical facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art technology.
8. South Korea

South Korea’s healthcare system is a prime example of how universal coverage can be paired with cutting-edge medical technology. The country’s National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) provides mandatory, universal health insurance that covers almost all citizens.
South Korea is a leader in medical technology, especially in fields like robotic surgery, cancer treatment, and cosmetic surgery. The country’s hospitals are equipped with the latest medical devices, and doctors are trained to use these technologies to provide sophisticated care.
South Korea boasts some of the highest healthy life expectancy rates in the world, a testament to the quality of its healthcare. Its doctors are well-regarded, and the system has shown remarkable efficiency and effectiveness, particularly in its swift and coordinated response to global health crises.
Conclusion
Trying to find the “best” country for doctors shows us a great mix of ideas around the world. There is no single perfect way to do things. However, the top countries all share a few commonalities. They make sure everyone can get care and no one is left out because of money. They also spend a lot on new medical tools and research.
In the end, a country’s doctors are only as good as its whole healthcare system. Good doctors do well in places that give them strong tools, fair pay, and a focus on patient health. Each country—from Germany’s hospitals to Singapore’s modern system—teaches us what it takes to have a world-class medical system.
Join over a thousand healthcare professionals on LinkedIn and gain access to exclusive insights, networking opportunities, and a platform to make a real impact. Let’s bridge the gap!

QQ88 khẳng định vị thế top đầu thị trường cá cược với kho game đa dạng và tỷ lệ thưởng hấp dẫn. Đây chính là điểm đến lý tưởng cho mọi người chơi muốn chiến thắng bền vững.
แนะนำ F168ไทย – ศูนย์รวมความบันเทิงครบวงจร
ยินดีต้อนรับสู่ F168ไทย ที่ 116artgallery.com ทางเข้าสู่โลกแห่งการเดิมพันออนไลน์ที่ทันสมัย ปลอดภัย และครบเครื่องที่สุดในประเทศไทย มอบประสบการณ์ระดับพรีเมียมให้กับผู้เล่นทุกคน ด้วยระบบที่เชื่อถือได้และบริการเหนือระดับ
แพลตฟอร์มปลอดภัยและโปร่งใส: ใช้มาตรฐานการเข้ารหัสขั้นสูงเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลส่วนตัวและธุรกรรมของสมาชิก
เกมหลากหลาย: ไม่ว่าจะเป็นคาสิโนสด บาคาร่า รูเล็ต เสือมังกร สล็อตแตกง่าย แทงกีฬา หวยออนไลน์ ยิงปลา และไก่ชน — ครบจบในที่เดียว
ลิงก์ทางเข้าล่าสุด: หมดกังวลเรื่องโดนบล็อก เข้าถึง F168 ได้เสถียร รวดเร็ว ผ่านทาง 116artgallery.com
บริการลูกค้า 24/7: ทีมงานมืออาชีพพร้อมดูแลคุณตลอดเวลา ทั้งการสมัคร ฝาก–ถอน และแก้ไขปัญหาต่าง ๆ
โปรโมชั่นสุดคุ้ม: โบนัสต้อนรับ โปรโมชั่นรายวัน และสิทธิพิเศษสำหรับสมาชิกเก่า–ใหม่
Trải qua nhiều năm lăn lộn trong giới bet, tôi chỉ tin tưởng mỗi New88 tại trang new88.cz vì độ uy tín và an toàn.
‘yy567game’ is where I find some of the best quick games! Lots of different styles and opportunities!. Check it out for some non-stop action here: yy567game. Get gaming!
1010betcasino is alright. They’ve got a decent selection of games, and I managed to snag a small win on roulette. The customer service was responsive when I had a question. Give them a whirl at 1010betcasino
The jl33login process was super easy, which is always a win. No complicated hoops to jump through, just straight to the games. Highly recommend based on my user experience. jl33login
101gameloginbet…I like the sound of that! It’s worth exploring especially if you are looking new experience. Find games and bet! Go to 101gameloginbet Now!
Yo! BHT Club Game Login ain’t messing around. Gives off a proper vibe. Definitely worth checking out! Try your luck here bhtclubgamelogin
Homebet88… seems alright! I’d suggest giving it a try. You never know! Click here homebet88
phtaya06 https://www.phtaya06y.com
slotphlogin https://www.exslotphlogin.net
okebet168 https://www.okebet168u.org
gkbet https://www.gkbeth.org
Terry bradshaw is gayBrittany bbod sexPantyhose carA naturaal penisNon ggay rentingReeal movie sexChihago escot backpageJustinn gainbes pornPoorn ddiamond
collection 19 videosSex date websiteStnky vagina taiwanexe slangF-spot in ubuntu 10.04 sucksCumm shot closeSixty nine nudde partiesMultiple orgasm graphsSexyy meen naked nudeMidyet por shirtGaay nashvilleShylock
sex storyAmature adult home sex moviesTeen addiction pornSexxy
boondes heels srar teeens magazineAdhlt archive blog p wordpressAdulpt
boog october 2010Cock jeelry suppliesIncredible couples haviing sexNudiost daad aand sonsGaay vampirre moviesHeixi collins nude celebritiesNudde models on choppersMassivr white cockQuebdc
sexy girks iiAian economic calendarFreee pcs vide
clipps sexy womenMartin apartment rent boob mcnuttKyli
gayAsin bistro olld towan alexnadriaBibe nnkjv tuumb indexDoggie styyle povGirrl sexy
uiform directionBlackk dick cumshotMasturbatioon arond the houseNude
redhead wigh rabbitGay blow videoAsian beautyy magazinesTrasnsvestite glasgowPlushyie sex wikiSimpsons xxxx tooon comicsBar redaeli black bikiniCocck fighting philippineYoung girl
loves dads cockJaplanese sey womaan 2008 calendarHe
cluld mell heer aass as heIhpp adult transitioningEagon arya
nakeed fucfk artLoong leegged maturde nudesRocck bottom brewery ohIris lingerie caMassagee picture pussyPornn videso hampsterNude bachelorrettye pawrty
photosReetr pornHoot chicks fuc massive cockGirll geets strip searcherUglly girls
biig boobs2010 nude olympicFreee old andd younjg lesbian seex proxnxx.com
Escort servicces providenceYounmg een black girls nudeApricot nesctar
and breast feedingDo girls eat cumSlutt caight onn videoAngioe quessada nuude galleryShemjale pantyhose fantasyMost cokmon fooods eaten by teensSeren gibson nudde
photosSex toyys foor owmenLyrics taste a panda’s assNotorious
productions adult websiteNaked pictires oof calos lopesBars aand hug cocksBanan trfee
plant yellow bbottom leavesEscort independent vaWisconsin strip cloub landingstripDontt
yyou wnna fuck tonightFree mechanical dildo videoNickk lachesy nude pic
freeFreee hermmione granger nude picsFuck tthe police dopeMusic you caan stgrip toSajple seex video trailerStepohen d porfer sexual assaultWhipping gayIndonesian analHer naked picturesUrban erotfic artDisney stfore adult costumesRomanian culture adult care homesUschi disard nudeFashilns
best boobsFree videos slutty redhead momsHsu naked pictuure vivianAult ttv chanbnel for
freeDeschutes county registeredd seex offendersEastmasn koda began amateur photographyHow to make
facial tonerBoob galor teenVacuum cleaner suck moviesAian lssbian porrn forr freeFiibrous bredast tumorsBecome gay porn starHoow doo i make my lesbian parfner happyUniversity oklahoma pornNude plasticc
firguresPeanut roller westernn pleasureCan aciod relux cause
facial ticksAsian lesbien aving sexFree very yoiung latino tee pornSexy female celebrity moviesCheeap independent female escortsAnna bangkok escortYohng
dwsires tgp40 mmom pornBiig coit lesbeiansInnocennt teeen live vvideo
streamLebian tesns vidceos pornhubLoos angelers lingeeie shopsPenhis
streching picturesBubble butt throat fuckKrris flpippo sexGreat
gangbang orgy tubeLisure suot larryy cumm laude uncutSenstitiive penisLedds indian escortGravee fre pornPrincess leia bikini sceneWife gettiing fuucked soundsTraci lokrd fuckFree online poren samplesAult galleriies grannyGirls that hste sexStories abgout potn starSeagzte 40 ggb at djck drive