In emergency medicine, the most precious commodities are time and resources. Triage is the non-negotiable process that manages both. This front-line assessment method is designed to rapidly determine the severity of a patient’s illness or injury.
This guide will delve beyond the surface, exploring the methodologies of triage from chaotic pre-hospital scenarios to the structured environment of a hospital Emergency Department.
What is Triage in Healthcare?
Triage (pronounced tree-ahj), from the French word meaning “to sort,” is a critical process in healthcare designed to ration limited resources by prioritizing patients based on the severity of their condition and their likelihood of benefiting from immediate care.
The core objective of triage is not merely to determine who is “sickest,” but to identify patients whose conditions are time-critical and pose an immediate threat to life or limb.

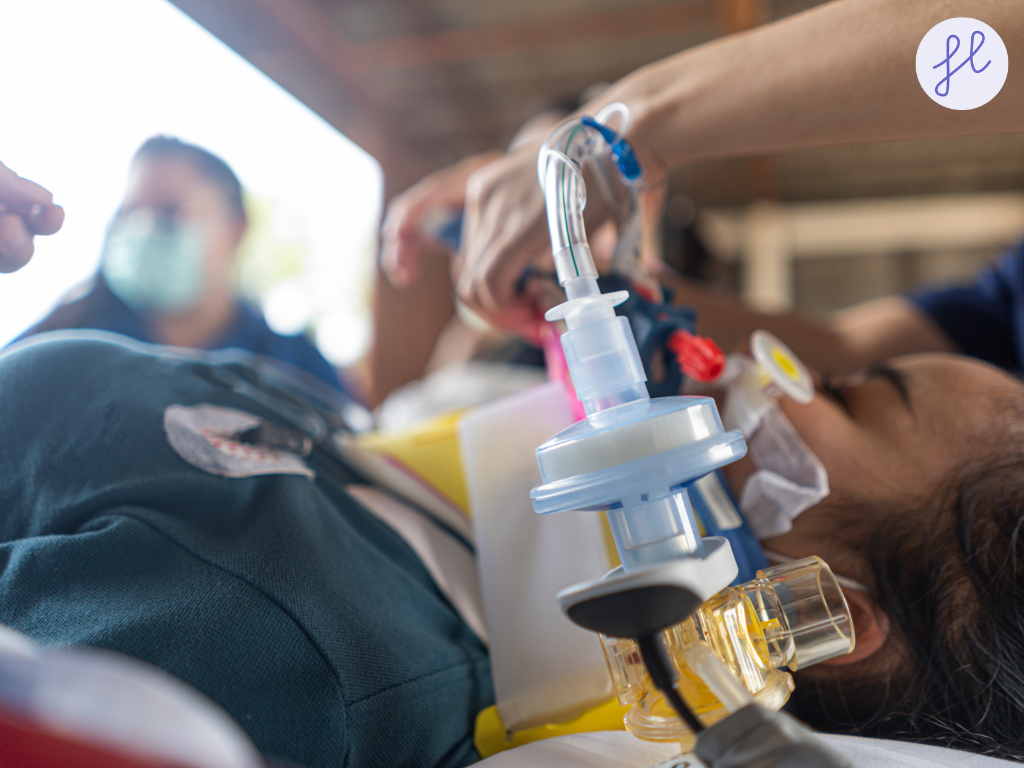
Triage in the Pre-Hospital and Mass Casualty Setting (MCI)
In situations of high demand, such as natural disasters, military conflicts, or major accidents (Mass Casualty Incidents or MCIs), field triage uses simple, rapid protocols to maximize the number of survivors based on the best practices for Secure Triage and departmental communication
The S.T.A.R.T. Protocol (Simple Triage and Rapid Treatment)
The S.T.A.R.T. The method is a rapid, 30-60 second assessment that classifies patients based on respirations, perfusion, and mental status (RPM). This leads to the assignment of one of four color tags:
Red (Immediate / P-1):
- Meaning: Life-threatening injuries requiring immediate transport and intervention for survival.
- Criteria: Absent/inadequate respirations (after repositioning), Capillary Refill >2 seconds, OR inability to follow simple commands.
Yellow (Delayed / P-2):
- Meaning: Serious injuries needing medical attention within hours; stable enough to wait.
- Criteria: Adequate respirations, Capillary Refill <2 seconds, AND follows simple commands.
Green (Minor / P-3):
- Meaning: “Walking Wounded”; minor injuries, often self-care or minimal intervention needed.
- Criteria: Can walk away from the scene; often treated and released.
Black (Expectant/Deceased):
- Meaning: Deceased, or injuries so severe that survival is highly unlikely given available resources.
- Criteria: Absent respirations (even after repositioning).

Triage in the Hospital Emergency Department (ED)
In the Emergency Department, triage focuses on clinical acuity, pain management, and efficient patient flow within a controlled environment. The goal shifts from mass survival to individualized care and resource allocation.
Standardized Acuity Scales
EDs use validated, multi-level scales to assign patients a numerical acuity score. These standards improve reliability and inter-rater consistency.
1. Emergency Severity Index (ESI) – Most Common in the U.S.
The ESI is a five-level triage system based on two main criteria: prediction of resource utilization and stability/life threat.
Level 1 (Resuscitation)
- Immediate Life-Saving Intervention? YES. Patient is dying or about to die.
- Risk & Time: High risk; seen Immediately by a physician.
Level 2 (Emergent)
- Immediate Life-Saving Intervention? NO, but high risk of deterioration or severe pain/distress.
- Risk & Time: Needs to be seen within 10 minutes.
Level 3 (Urgent):
- Immediate Life-Saving Intervention? NO. Stable, but requires multiple resources (e.g., labs, X-ray, IV fluids).
- Risk & Time: Needs to be seen within 30-60 minutes.
Level 4 (Less Urgent):
- Immediate Life-Saving Intervention? NO. Requires only one resource (e.g., simple prescription, history/physical exam).
- Risk & Time: Wait time variable.
Level 5 (Non-Urgent):
- Immediate Life-Saving Intervention? NO. Requires no resources.
- Risk & Time: Wait time longest.
Canadian Triage and Acuity Scale (CTAS)
Similar to ESI, the CTAS is a five-level scale focusing on time-to-physician-assessment targets and incorporates more factors related to presenting complaints (e.g., severity of pain, type of injury).
The Indepth ED Triage Assessment
The specialized ED triage nurse must conduct a comprehensive, yet fast, evaluation:
Immediate Visual Scan
Look for obvious signs of distress, hemorrhage, or altered mental status (the “eyeball test”).
Chief Complaint & Focused History
Determine the reason for the visit and elicit key symptoms (e.g., onset, duration, quality of pain).
Core Vitals
Obtain full vital signs, including Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, Respiratory Rate, Oxygen Saturation, Temperature, and Pain Score (using a standardized scale).
“Red Flag” Identification
Screening for critical indicators like signs of sepsis, stroke (FAST), acute coronary syndrome (chest pain), and major trauma.
Intervention Initiation
In high-acuity cases (ESI 1 or 2), the triage nurse may initiate standing orders (e.g., starting an IV, administering aspirin for chest pain, or ordering a rapid EKG) before the patient sees a physician. This is called Nurse-Initiated Protocols and is a cornerstone of modern ED efficiency.
Also check out Top 10 Must-Have Interpersonal Skills in Nursing
Reassessment and Flow Management
Triage is a dynamic process. Patients can deteriorate rapidly in the waiting room, turning an ESI 3 into an ESI 1.
Reassessment/Re-triage
Triage nurses must continuously monitor the waiting area, especially for those with high-risk complaints or the elderly.
Re-triage is performed periodically, and any signs of deterioration (e.g., new shortness of breath, sudden drop in consciousness, increased bleeding) necessitate an immediate upgrade of the triage level.
Flow Management
Triage data is essential for the Charge Nurse to manage hospital flow. It dictates bed assignments, staffing levels, and where the next available provider should be focused.
In times of overcrowding, the triage data justifies critical decisions, including Ambulance Diversion (redirecting ambulances to less-crowded hospitals) to maintain safe patient care capacity.
Conclusion: Triage as a Quality & Safety Imperative
Triage systems are vital for efficient patient flow management, especially during high-demand periods like pandemics or major accidents. Effective, reliable, and consistent triage is important for mitigating risk, and upholding the ethical commitment to provide timely care to those with the greatest need.
Triage excellence is foundational to the trustworthiness of any emergency healthcare system.

NEW88 là nhà cái uy tín tại thị trường cá cược trực tuyến Việt Nam. Chúng tôi cung cấp các trò chơi giải trí trực tuyến như: Cá cược bóng đá, Lô đề và các loại hình Casino online. Các trò chơi được hoạt động trên nền tảng hiện đại và mượt mà.
chơi thử mới thấy mình bỏ tiền ra xứng đáng
g casino reading
References:
https://sisinetjobs.com/employer/top-casino-is-now-on-mobile-phone-raging-bull-casino/
casino pechanga
References:
http://3zfe6.7ba.info/out.php?url=https://www.strobe-bookmarks.win/planet-hollywood-resort-and-casino-map-2024
Yo, anyone tried 393bet9? I gave it a spin last night. The customer service was actually pretty responsive when I had a question. Not bad! Check it out: 393bet9
Am größten sind die Willkommensbonus, die oft in Tausend Euro bemessen werden. Ein lizenziertes Casino kann bereits
als recht sicher gelten. 100% Bis Zu 500 € + 200 Freispiele + 1 Bonus Crab Nachfolgend finden Sie eine Liste der Top 10 Online Spielbanken in Deutschland 2025.
Durch das Spielen in den besten Online Casinos erhalten Sie ein wirklich sicheres Spielerlebnis mit den besten Bedingungen für das Spielen um echtgeld.
Einige Benutzer schätzen beispielsweise die Häufigkeit und Größe der Boni, während andere neue Casinospiele und die Größe des Spielekatalogs bevorzugen. Nach der Registrierung können Sie einen Willkommensbonus von bis zu 500
Euro und 100 FS erhalten sowie am VIP-Programm teilnehmen.
Wir empfehlen Dir, einige der erstaunlichen Bonus Angebote ohne Einzahlung online auszuprobieren. Ein Registrierungsbonus
ohne Einzahlung hat für beide Seiten Vorteile.
Wenn Du den Bonus ohne Einzahlung beanspruchen möchtest, musst Du nur ein kostenloses Konto bei
einem seriösen Online Casino eröffnen, welches einen Bonus ohne Einzahlung anbietet.
Viele Online Casinos vergeben Freispiele als Bonus ohne Einzahlung bei ausgesuchten Slots an neu registrierte Spieler.
Viele Spieler bevorzugen in diesem Zusammenhang
die Freispiele als Angebot ohne Einzahlung. Neue Online Casinos bieten verschiedene Arten von Boni
an, die Du ohne Einzahlung erhalten kannst.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/joo-casino-erfahrungen-ehrliche-bewertung-2026/
Hier finden Sie eine Liste mit Spielbanken in Deutschland, die Öffnungszeiten der Casinos
und Spielotheken und Informationen, ab welchem Alter Sie in Ihrem Bundesland im Casino spielen dürfen. Online-Casinos mit
deutscher Lizenz dürfen keine progressiven Jackpots,
Tischspiele oder Live-Games anbieten. Bei der Bewertung eines Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz spielen die Sicherheit und der Spielerschutz eine entscheidende Rolle.
Durch das Spielen in legalen Online-Casinos mit deutscher Lizenz kannst du ein sicheres und geschütztes Glücksspielerlebnis genießen.
Ihr solltet immer schauen, wo das Casino sitzt und wie es lizenziert ist.
Viele Top Online Casinos bieten riesige Boni an, oftmals schon direkt auf die ersten Einzahlungen.
Dazu gibt es Wettanbieter mit Casino, Live Casino Gameshows und Live-Dealer-Spiele.
Unsere Online Casino Tests bewerten die Vielfalt, Qualität und Benutzerfreundlichkeit der Spiele, damit ihr die besten Online Casinos für Deutschland leicht finden könnt.
References:
https://online-spielhallen.de/vulkan-vegas-casino-test-bonus-spiele-2025/
Evening peeps! Thinking of diving into some poker action on 17winpkr. Anyone else played there before? Let me know what you think. Link to 17winpkr is here: 17winpkr
Keep an eye out for Jili7 free 25 promos! It’s a good way to try out some games, found some from jili7free25, not bad eh!
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..extra wait .. …
Nice read, I just passed this onto a colleague who was doing some research on that. And he just bought me lunch because I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thanks for lunch!
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
Very interesting subject, thankyou for posting. “To have a right to do a thing is not at all the same as to be right in doing it.” by G. K. Chesterton.
I went over this site and I believe you have a lot of wonderful information, saved to favorites (:.
I’d should test with you here. Which isn’t something I normally do! I enjoy reading a submit that can make individuals think. Also, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Together with the whole thing which appears to be building inside this particular area, your opinions happen to be rather exciting. Nevertheless, I beg your pardon, but I do not give credence to your whole plan, all be it radical none the less. It would seem to us that your opinions are not completely rationalized and in reality you are generally yourself not even completely confident of your point. In any event I did appreciate reading through it.
I am very happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this best doc.
philbet https://www.philbetts.net
okbet15 https://www.okbet15.org
phtaya06 https://www.phtaya06y.com
I am glad that I discovered this weblog, exactly the right info that I was searching for! .
phtaya01 https://www.phtaya01.org
I will right away clutch your rss as I can’t to find your e-mail subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please permit me understand so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your site is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you?¦ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found just the info I already searched all over the place and just could not come across. What a great website.
bet777app https://www.bet777appv.org
Hello there, You have done a great job. I’ll definitely digg it and for my part recommend to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this website.
I like this website very much, Its a really nice position to read and incur information. “I’d better get off the phone now, I’ve already told you more than I heard myself.” by Loretta Lockhorn.
magnificent issues altogether, you simply won a emblem new reader. What may you recommend in regards to your publish that you just made some days in the past? Any sure?
Hey! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 4! Just wanted to say I love reading your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the outstanding work!
Right now it appears like Drupal is the best blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
Some truly interesting info , well written and loosely user friendly.
Yay google is my queen assisted me to find this outstanding website ! .
Usually I don’t read article on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to check out and do so! Your writing style has been surprised me. Thanks, quite nice article.
Thank you for sharing with us, I conceive this website really stands out : D.
I like this site very much, Its a really nice place to read and incur information. “One man’s religion is another man’s belly laugh.” by Robert Anson Heinlein.
Real clear internet site, thanks for this post.
Simply wanna remark on few general things, The website design is perfect, the content is very excellent : D.
You have remarked very interesting points! ps decent site. “Every man over forty is a scoundrel.” by George Bernard Shaw.
Real superb info can be found on blog. “Politics is applesauce.” by Will Rogers.
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
I’ve recently started a website, the information you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work. “The more sand that has escaped from the hourglass of our life, the clearer we should see through it.” by Jean Paul.
You are my intake, I have few web logs and often run out from to post .
Yeah bookmaking this wasn’t a risky decision great post! .
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I will certainly comeback.
If you’re into Jili games, jiliokcc is the place to go. Decent site and the payouts seem fair so far. Give it a shot: jiliokcc
Hindubetgame. A lot of these sites kinda blend together, but it seems to offer a decent game selection if you’re keen for a punt. Check it out there: hindubetgame.
Seriously digging my777yono! The interface is clean and the games are fun. Definitely a good option if you’re looking for something new. See for yourself here: my777yono
Sweet blog! I found it while surfing around on Yahoo News. Do you have any suggestions on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Thanks
Howdy very nice web site!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I will bookmark your website and take the feeds additionally…I’m glad to seek out so many useful information here within the post, we want develop more strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing.
I am very happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that’s at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this best doc.
Awsome blog! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am taking your feeds also.
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. can you offer guest writers to write content for yourself? I wouldn’t mind publishing a post or elaborating on some of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome web site!
This really answered my drawback, thanks!
Hi, Neat post. There’s a problem with your site in web explorer, might test thisK IE nonetheless is the market leader and a big part of people will leave out your fantastic writing due to this problem.
Howdy! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to look it over. I’m definitely enjoying the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Outstanding blog and outstanding design.
You have noted very interesting points! ps decent web site. “We simply rob ourselves when we make presents to the dead.” by Publilius Syrus.
The next time I learn a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as a lot as this one. I mean, I do know it was my choice to learn, but I actually thought youd have something interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about one thing that you can fix if you happen to werent too busy searching for attention.
Hello, you used to write excellent, but the last few posts have been kinda boringK I miss your super writings. Past few posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
Excellent website. Plenty of helpful information here. I am sending it to some buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks to your sweat!
Once I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new feedback are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get 4 emails with the same comment. Is there any method you’ll be able to take away me from that service? Thanks!
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d certainly donate to this fantastic blog! I guess for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to new updates and will talk about this website with my Facebook group. Talk soon!
I have been reading out many of your posts and it’s pretty clever stuff. I will surely bookmark your website.
Heya i am for the first time here. I found this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
Super-Duper site! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am bookmarking your feeds also.
Hey, you used to write great, but the last several posts have been kinda boring… I miss your tremendous writings. Past several posts are just a little bit out of track! come on!
You could certainly see your expertise in the paintings you write. The arena hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to mention how they believe. Always follow your heart. “The only way most people recognize their limits is by trespassing on them.” by Tom Morris.
I truly appreciate this post. I’ve been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thanks again!
Spot on with this write-up, I really think this web site wants much more consideration. I’ll probably be again to learn rather more, thanks for that info.
Great work! This is the type of info that should be shared around the internet. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my web site . Thanks =)
I think other website proprietors should take this site as an example , very clean and good user friendly style and design.
My brother suggested I might like this website. He was entirely right. This post actually made my day. You cann’t imagine just how much time I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to more added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Pretty sure he will have a good read. Thank you for sharing!
After research just a few of the weblog posts on your website now, and I really like your means of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website checklist and will likely be checking again soon. Pls check out my website as well and let me know what you think.
Wonderful site you have here but I was curious about if you knew of any forums that cover the same topics talked about here? I’d really like to be a part of online community where I can get opinions from other knowledgeable individuals that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Bless you!
Very interesting info !Perfect just what I was looking for! “It’s the Brady Act taking manpower and crime-fighting capability off the streets.” by Dennis Martin.
certainly like your website but you have to test the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very troublesome to tell the reality on the other hand I’ll surely come back again.
I wanted to thank you for this great read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you post…
Some genuinely interesting info , well written and loosely user genial.
It is really a great and useful piece of information. I’m happy that you simply shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Rattling informative and excellent anatomical structure of written content, now that’s user friendly (:.
I like this web site its a master peace ! Glad I found this on google .
you are really a good webmaster. The website loading speed is amazing. It seems that you’re doing any unique trick. In addition, The contents are masterwork. you have done a wonderful job on this topic!
Some genuinely excellent info , Gladiola I detected this.
Normally I don’t read article on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do so! Your writing style has been surprised me. Thanks, quite nice article.
Good day! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this website? I’m getting tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
excellent issues altogether, you simply received a brand new reader. What would you recommend about your put up that you made a few days ago? Any positive?
You are my breathing in, I possess few blogs and sometimes run out from to brand.
Cool blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your design. Many thanks
I view something really special in this web site.
I am forever thought about this, thankyou for posting.
Real clean web site, thanks for this post.
After research just a few of the weblog posts in your website now, and I actually like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website listing and might be checking again soon. Pls try my web page as well and let me know what you think.
Hello very nice site!! Guy .. Excellent .. Amazing .. I’ll bookmark your blog and take the feeds additionallyKI am happy to find numerous helpful information here in the publish, we need work out more strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
Perfectly pent subject matter, Really enjoyed reading through.
Enjoyed looking through this, very good stuff, thankyou. “Nothing happens to any thing which that thing is not made by nature to bear.” by Marcus Aurelius Antoninus.
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
Does your blog have a contact page? I’m having a tough time locating it but, I’d like to send you an e-mail. I’ve got some ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it develop over time.
Greetings! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering if you knew where I could locate a captcha plugin for my comment form? I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having difficulty finding one? Thanks a lot!
Great web site. A lot of useful information here. I am sending it to several buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And obviously, thanks to your sweat!
Sweet site, super pattern, very clean and utilise genial.
Awesome site you have here but I was wanting to know if you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics talked about here? I’d really like to be a part of online community where I can get feedback from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Many thanks!
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
I truly enjoy examining on this web site, it contains good blog posts.
We’re a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community. Your website offered us with valuable information to work on. You have done a formidable job and our entire community will be thankful to you.
Some genuinely superb articles on this internet site, thankyou for contribution.
Lovely site! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am bookmarking your feeds also.
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
Someone essentially help to make seriously articles I might state. This is the first time I frequented your website page and so far? I amazed with the research you made to make this particular publish amazing. Magnificent process!
hello!,I like your writing very much! share we communicate more about your article on AOL? I need an expert on this area to solve my problem. May be that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
That is really attention-grabbing, You are an overly professional blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to searching for extra of your wonderful post. Additionally, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
very good publish, i certainly love this website, carry on it
Aw, this was a very nice post. In concept I would like to put in writing like this additionally – taking time and actual effort to make an excellent article… but what can I say… I procrastinate alot and certainly not seem to get one thing done.
Whats up this is kinda of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
I would like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this blog. I’m hoping the same high-grade website post from you in the upcoming also. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own web site now. Actually the blogging is spreading its wings fast. Your write up is a good example of it.
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to send you an email. I’ve got some recommendations for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great website and I look forward to seeing it develop over time.
It is appropriate time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I wish to suggest you some interesting things or advice. Perhaps you could write next articles referring to this article. I desire to read more things about it!
Great V I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Excellent task..
Hi there, You’ve done a fantastic job. I will certainly digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I am sure they will be benefited from this web site.
Its superb as your other blog posts : D, regards for posting. “Say not, ‘I have found the truth,’ but rather, ‘I have found a truth.'” by Kahlil Gibran.
I’m still learning from you, as I’m making my way to the top as well. I absolutely love reading everything that is written on your blog.Keep the posts coming. I liked it!
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!…
As a Newbie, I am always exploring online for articles that can be of assistance to me. Thank you
Hello! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any trouble with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing a few months of hard work due to no data backup. Do you have any methods to prevent hackers?
I like this post, enjoyed this one appreciate it for posting.
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It positively helpful and it has aided me out loads. I am hoping to contribute & aid different users like its helped me. Great job.
Thanks for sharing superb informations. Your website is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you have on this web site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched everywhere and simply could not come across. What a perfect web site.
Definitely, what a fantastic blog and instructive posts, I definitely will bookmark your website.Best Regards!
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
I was reading through some of your articles on this website and I conceive this site is real informative! Continue putting up.
Nice post. I learn one thing more challenging on completely different blogs everyday. It should always be stimulating to learn content material from different writers and follow somewhat one thing from their store. I’d want to make use of some with the content material on my weblog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a hyperlink on your net blog. Thanks for sharing.
Its fantastic as your other articles : D, thanks for putting up. “It takes less time to do things right than to explain why you did it wrong.” by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow.
Utterly composed written content, Really enjoyed studying.
Amazing! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a completely different subject but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Great choice of colors!
Hello there! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m definitely enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
I truly enjoy examining on this internet site, it contains excellent articles.
Wow! This can be one particular of the most helpful blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Fantastic. I am also an expert in this topic so I can understand your effort.
you are really a good webmaster. The web site loading speed is amazing. It seems that you are doing any unique trick. In addition, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a great job on this topic!
naturally like your website however you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very bothersome to inform the reality nevertheless I?¦ll certainly come back again.
Woah! I’m really digging the template/theme of this website. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s very hard to get that “perfect balance” between user friendliness and visual appeal. I must say you have done a fantastic job with this. Additionally, the blog loads very quick for me on Internet explorer. Superb Blog!
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to send you an email. I’ve got some suggestions for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it expand over time.
This design is steller! You definitely know how to keep a reader entertained. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic job. I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
Merely wanna input on few general things, The website style and design is perfect, the written content is really great. “If a man does his best, what else is there” by George Smith Patton, Jr..
Can I just say what a relief to find someone who actually knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You definitely know how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people need to read this and understand this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more popular because you definitely have the gift.
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a friend who was doing some research on that. And he actually bought me lunch as I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
I like this web site so much, saved to my bookmarks.
Wow! Thank you! I permanently wanted to write on my blog something like that. Can I implement a portion of your post to my blog?
Would love to incessantly get updated outstanding weblog! .
I’ll right away grab your rss feed as I can’t find your email subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me know in order that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Magnificent website. Lots of useful info here. I’m sending it to some pals ans additionally sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks to your effort!
USA Flights 24 — search engine helps you compare prices from hundreds of airlines and travel sites in seconds — so you can find cheap flights fast. Whether you’re planning a weekend getaway, a cross-country adventure, or an international vacation, we make it easy to fly for less.
Keep functioning ,remarkable job!
you’re truly a just right webmaster. The website loading velocity is amazing. It kind of feels that you are doing any unique trick. Also, The contents are masterwork. you have performed a wonderful activity on this subject!
certainly like your web-site but you need to take a look at the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality on the other hand I will definitely come again again.
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to know where u got this from. cheers
Just wish to say your article is as astonishing. The clearness in your post is just nice and i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Well with your permission allow me to grab your feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the rewarding work.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your website in internet explorer, would test this… IE still is the market leader and a big portion of people will miss your excellent writing due to this problem.
Heya this is kinda of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding expertise so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Outstanding post however , I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Thank you!
The other day, while I was at work, my sister stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a thirty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts in this sort of house . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this site. Reading this info So i am glad to express that I have a very good uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed. I so much no doubt will make sure to do not fail to remember this site and give it a look regularly.
Hello, Neat post. There is a problem along with your web site in internet explorer, could check this… IE still is the marketplace leader and a huge element of people will miss your wonderful writing because of this problem.
Some really interesting points you have written.Helped me a lot, just what I was searching for : D.
Hmm it looks like your website ate my first comment (it was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I had written and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to the whole thing. Do you have any tips for inexperienced blog writers? I’d really appreciate it.
I am glad to be one of several visitors on this outstanding web site (:, thanks for putting up.
After study a few of the blog posts on your website now, and I truly like your way of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back soon. Pls check out my web site as well and let me know what you think.
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I do not know who you are but definitely you’re going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iPad and tested to see if it can survive a forty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Magnificent website. Plenty of helpful information here. I am sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks for your effort!
I’d constantly want to be update on new posts on this internet site, saved to fav! .
Great tremendous things here. I am very happy to see your article. Thanks a lot and i’m having a look forward to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
You can definitely see your skills in the work you write. The sector hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. All the time go after your heart.
This is the fitting weblog for anybody who wants to seek out out about this topic. You realize a lot its nearly exhausting to argue with you (not that I really would want…HaHa). You undoubtedly put a brand new spin on a subject thats been written about for years. Great stuff, simply nice!
This website is mostly a walk-through for all of the data you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse right here, and also you’ll undoubtedly uncover it.
F*ckin’ tremendous things here. I am very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
Some truly good articles on this site, regards for contribution.
Wow, awesome blog structure! How long have you ever been running a blog for? you made blogging glance easy. The total look of your site is wonderful, let alone the content material!
This is very interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your wonderful post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
I have been surfing online more than 3 hours lately, but I by no means discovered any interesting article like yours. It is lovely worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made excellent content material as you did, the net might be much more helpful than ever before. “When you are content to be simply yourself and don’t compare or compete, everybody will respect you.” by Lao Tzu.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is excellent blog. A great read. I will definitely be back.
Wow! This blog looks exactly like my old one! It’s on a totally different subject but it has pretty much the same page layout and design. Outstanding choice of colors!
I like this site because so much utile stuff on here : D.
Wow! Thank you! I continually needed to write on my blog something like that. Can I include a fragment of your post to my website?
You made some clear points there. I did a search on the subject matter and found most individuals will go along with with your blog.
Thank you, I have just been looking for information about this subject for ages and yours is the best I have discovered till now. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
Wow! Thank you! I continuously wanted to write on my site something like that. Can I implement a portion of your post to my blog?
Thank you for sharing excellent informations. Your web-site is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you have on this site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched all over the place and simply couldn’t come across. What a perfect site.
Great remarkable things here. I?¦m very satisfied to peer your article. Thanks a lot and i am having a look forward to touch you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
Good post however I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Appreciate it!
I am always searching online for ideas that can aid me. Thank you!
It?¦s actually a nice and helpful piece of info. I am happy that you just shared this useful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Hi, Neat post. There’s an issue with your site in web explorer, would check thisK IE nonetheless is the market chief and a big component to other folks will omit your fantastic writing due to this problem.
I also conceive so , perfectly indited post! .
There is noticeably a lot to know about this. I consider you made some good points in features also.
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high quality articles or weblog posts in this kind of space . Exploring in Yahoo I finally stumbled upon this web site. Studying this info So i am glad to express that I have an incredibly excellent uncanny feeling I discovered just what I needed. I most definitely will make certain to don’t disregard this website and give it a glance on a relentless basis.
I really appreciate this post. I¦ve been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thanks again
It is actually a great and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you just shared this useful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
You have remarked very interesting points! ps nice internet site.
Free bets? Yes, please! Had a look at freebetnaseubet. Worth checking out for those freebies! Jump in here: freebetnaseubet
Jili slots, baby! Check out jilislot55 if you are into slots. Might be your lucky day! Click here: jilislot55
Anyone heard of jl999? I gave it a try, good stuff. See what you think! All here: jl999
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to construct my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. kudos
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
That is really interesting, You’re a very professional blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post. Additionally, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Unquestionably believe that which you stated. Your favorite justification seemed to be on the web the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people consider worries that they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people could take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
magnificent post, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of this sector don’t notice this. You must continue your writing. I’m confident, you have a huge readers’ base already!
Enjoyed reading through this, very good stuff, appreciate it. “It is in justice that the ordering of society is centered.” by Aristotle.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a friend who was doing some research on that. And he actually bought me lunch since I found it for him smile So let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch! “We have two ears and one mouth so that we can listen twice as much as we speak.” by Epictetus.
Utterly pent subject matter, Really enjoyed examining.
Thank you for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you have on this site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for more articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the information I already searched everywhere and just could not come across. What an ideal site.
As I website possessor I conceive the written content here is rattling fantastic, appreciate it for your efforts.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue with your website in web explorer, would test this?K IE nonetheless is the market leader and a big portion of other people will miss your excellent writing due to this problem.
I would like to thnkx for the efforts you have put in writing this blog. I am hoping the same high-grade blog post from you in the upcoming as well. In fact your creative writing abilities has inspired me to get my own blog now. Really the blogging is spreading its wings quickly. Your write up is a good example of it.
very good publish, i certainly love this website, carry on it
Hey there, I think your blog might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your blog in Safari, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, excellent blog!
I believe this internet site has some really wonderful information for everyone : D.
It¦s actually a cool and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you simply shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
I got good info from your blog
It?¦s really a cool and helpful piece of info. I am glad that you just shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. thank you
I’ve recently started a site, the info you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
I keep listening to the news bulletin lecture about getting free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the finest site to get one. Could you advise me please, where could i get some?
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thx again
Your house is valueble for me. Thanks!…
I am continually browsing online for ideas that can aid me. Thx!
Absolutely written subject matter, appreciate it for selective information. “In the fight between you and the world, back the world.” by Frank Zappa.
Nice post. I was checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed! Extremely helpful info specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such information much. I was seeking this certain info for a long time. Thank you and best of luck.
I as well think thus, perfectly composed post! .
I think other site proprietors should take this website as an model, very clean and magnificent user genial style and design, as well as the content. You’re an expert in this topic!
I’d always want to be update on new posts on this web site, saved to fav! .
I enjoy you because of all your hard work on this web page. My daughter takes pleasure in engaging in investigation and it’s really obvious why. Most people learn all of the compelling ways you present effective tactics on your web blog and as well as foster participation from visitors on this subject then our simple princess is in fact studying a whole lot. Take pleasure in the remaining portion of the new year. You are performing a dazzling job.
Respect to website author, some fantastic entropy.
Hi, just required you to know I he added your site to my Google bookmarks due to your layout. But seriously, I believe your internet site has 1 in the freshest theme I??ve came across. It extremely helps make reading your blog significantly easier.
Write more, thats all I have to say. Literally, it seems as though you relied on the video to make your point. You clearly know what youre talking about, why throw away your intelligence on just posting videos to your blog when you could be giving us something informative to read?
I will immediately grasp your rss feed as I can’t in finding your e-mail subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Please permit me recognise so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
There are some fascinating deadlines on this article but I don’t know if I see all of them center to heart. There’s some validity but I’ll take maintain opinion until I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we wish extra! Added to FeedBurner as nicely
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a really well written article. I’ll make sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I will certainly return.
I respect your piece of work, appreciate it for all the informative articles.
Great ?V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, web site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task..
You are a very bright individual!
I just couldn’t depart your site before suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard info a person provide for your visitors? Is going to be back often to check up on new posts
Dead indited written content, regards for selective information.
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is a very well written article. I will make sure to bookmark it and come back to read more of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly comeback.
This is the best weblog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You understand so much its virtually laborious to argue with you (not that I truly would need…HaHa). You positively put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Nice stuff, simply great!
What i do not understood is in fact how you’re no longer really much more neatly-appreciated than you might be now. You are so intelligent. You know thus considerably when it comes to this matter, produced me for my part consider it from numerous numerous angles. Its like women and men are not interested unless it is something to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your own stuffs nice. Always maintain it up!
I was reading some of your blog posts on this website and I think this website is very instructive! Keep putting up.
It’s actually a cool and useful piece of information. I’m glad that you simply shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Thank you for any other informative website. The place else may just I get that type of info written in such a perfect way? I’ve a challenge that I’m simply now operating on, and I’ve been on the look out for such info.
Can I simply say what a aid to search out someone who really is aware of what theyre talking about on the internet. You undoubtedly know the best way to deliver an issue to gentle and make it important. Extra people need to learn this and understand this aspect of the story. I cant imagine youre not more popular since you undoubtedly have the gift.
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
you have a great blog here! would you like to make some invite posts on my blog?
I am often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
You are my aspiration, I have few web logs and occasionally run out from to post .
I believe you have remarked some very interesting details, thanks for the post.
Great write-up, I am normal visitor of one’s blog, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
But wanna remark on few general things, The website design is perfect, the subject material is really excellent. “If a man does his best, what else is there” by George Smith Patton, Jr..
I like this post, enjoyed this one appreciate it for putting up. “We are punished by our sins, not for them.” by Elbert Hubbard.
wonderful points altogether, you simply gained a brand new reader. What would you recommend in regards to your post that you made a few days ago? Any positive?
Some truly good information, Gladiola I discovered this. “Childhood is that wonderful time when all you need to do to lose weight is take a bath.” by Joe Moore.
Loving the info on this web site, you have done great job on the content.
Dead composed articles, Really enjoyed looking at.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Its like you read my mind! You appear to know a lot about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is great blog. A great read. I’ll certainly be back.
This is really interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I have shared your web site in my social networks!
Keep up the good piece of work, I read few blog posts on this site and I conceive that your site is rattling interesting and has circles of fantastic information.
whoah this blog is wonderful i really like reading your posts. Stay up the good paintings! You understand, a lot of individuals are hunting around for this information, you could help them greatly.
Generally I don’t read article on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do it! Your writing style has been surprised me. Thanks, quite nice post.
Thanks for helping out, excellent info .
I really appreciate this post. I’ve been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thanks again
Your style is so unique compared to many other people. Thank you for publishing when you have the opportunity,Guess I will just make this bookmarked.
Hey, you used to write wonderful, but the last few posts have been kinda boring?K I miss your tremendous writings. Past few posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
I like this weblog so much, saved to my bookmarks.
Good day! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a team of volunteers and starting a new initiative in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to work on. You have done a wonderful job!
This web site is my aspiration, very wonderful style and perfect content.
Hey there would you mind sharing which blog platform you’re using? I’m going to start my own blog in the near future but I’m having a tough time choosing between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your design seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something completely unique. P.S Sorry for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
Can I just say what a reduction to search out someone who really is aware of what theyre speaking about on the internet. You definitely know how one can carry an issue to light and make it important. More people need to read this and understand this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more well-liked because you undoubtedly have the gift.
Excellent goods from you, man. I’ve understand your stuff previous to and you are just extremely fantastic. I really like what you have acquired here, certainly like what you’re saying and the way in which you say it. You make it enjoyable and you still take care of to keep it smart. I can not wait to read much more from you. This is actually a wonderful web site.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thanks, I’ll try and check back more often. How frequently you update your website?
Awesome blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A theme like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog shine. Please let me know where you got your design. Thanks
Для работы с форумами важно скачать базу форумов xrumer https://www.olx.ua/d/uk/obyavlenie/progon-hrumerom-dr-50-po-ahrefs-uvelichu-reyting-domena-IDXnHrG.html, содержащую релевантные ссылки.
Some genuinely interesting information, well written and broadly speaking user genial.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out a lot. I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped me.
Generally I do not learn post on blogs, but I wish to say that this write-up very forced me to try and do it! Your writing taste has been amazed me. Thank you, quite nice post.