Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) redefined how healthcare is delivered and experienced. With the integration of advanced technologies, RPM enables healthcare providers to monitor patients outside traditional clinical settings, offering real-time insights and proactive care.
This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of RPM, from its core principles to its benefits, challenges, and future potential.
Remote Patient Monitoring
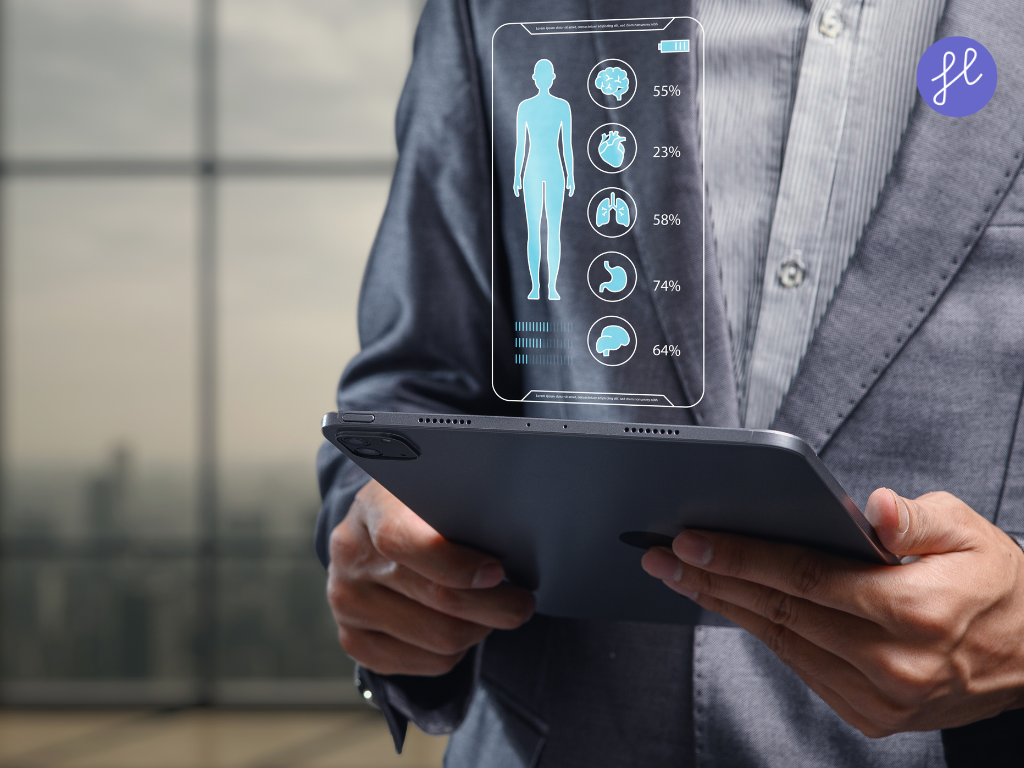

Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a healthcare delivery method that uses digital technologies to monitor and capture health data from patients in one location (usually their home) and electronically transmit that information to healthcare providers in a different location for assessment and recommendations.
Unlike traditional telehealth, which often focuses on real-time video consultations, RPM is about continuous data collection. It allows clinicians to keep a “digital eye” on a patient’s vital signs without the patient needing to leave their house
Key Components of RPM
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and biosensors that collect vital signs.
- Mobile Health Apps: Applications that allow patients to input data manually or sync with devices.
- Cloud-Based Platforms: Secure systems that store and analyze patient data.
- Healthcare Portals: Interfaces for clinicians to access and interpret patient information.
Common Health Metrics Tracked via RPM:
- Blood Pressure: Essential for managing hypertension.
- Blood Glucose: Critical for diabetes management.
- Heart Rate & ECG: Used for detecting arrhythmias or post-cardiac surgery recovery.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): Important for COPD and COVID-19 recovery.
- Weight: Often used to monitor fluid retention in congestive heart failure (CHF) patients.
How Does RPM Work?
Remote Patient Monitoring relies on a seamless loop of data and communication. Here is the typical workflow:
- Device Setup: A patient is issued a specialized medical device (like a smart scale or blood pressure cuff) that is Bluetooth or cellular-enabled.
- Data Collection: The patient uses the device as instructed. The device automatically records the physiological data.
- Data Transmission: The data is transmitted via a secure cloud-based platform to the healthcare provider’s Electronic Health Record (EHR) system.
- Clinical Action: Providers review the data. If a reading falls outside of a predetermined “normal” range, the system triggers an alert, allowing the doctor to intervene before a medical emergency occurs.
Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
For Patients
- Convenience: No need for frequent hospital visits.
- Peace of Mind: Continuous monitoring reduces anxiety.
- Cost Savings: Fewer hospital admissions and ER visits.
- Improved Outcomes: Early detection leads to better management.
For Providers
- Data-Driven Decisions: Access to real-time data enhances diagnostic accuracy.
- Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and reduced administrative burden.
- Patient Engagement: Encourages active participation in health management.
- Reduced Readmissions: Proactive care prevents complications.
RPM vs. Telehealth: What’s the Difference?
While often used interchangeably, Remote Patient Monitoring and telehealth are distinct.
| Feature | RPM | Telehealth |
| Focus | Continuous data collection | Real-time communication |
| Tools | Wearables, sensors, apps | Video calls, messaging |
| Interaction | Asynchronous | Synchronous |
| Use Case | Chronic disease management | Consultations, follow-ups |
Learn more about telehealth and its role in modern care.
Applications of RPM in Healthcare
Chronic Disease Management
RPM is especially effective in managing long-term conditions such as:
- Diabetes: Continuous glucose monitoring and insulin tracking.
- Hypertension: Blood pressure cuffs that transmit readings.
- COPD: Oxygen saturation and respiratory rate monitoring.
- Heart Disease: ECG and heart rate tracking.
Post-Surgical Recovery
RPM allows for real-time monitoring of recovery progress, reducing complications and hospital readmissions.
Elderly Care
For aging populations, RPM provides a safety net, enabling independent living with continuous supervision.
Mental Health Monitoring
Wearables and apps track sleep patterns, activity levels, and mood indicators to support mental health interventions.
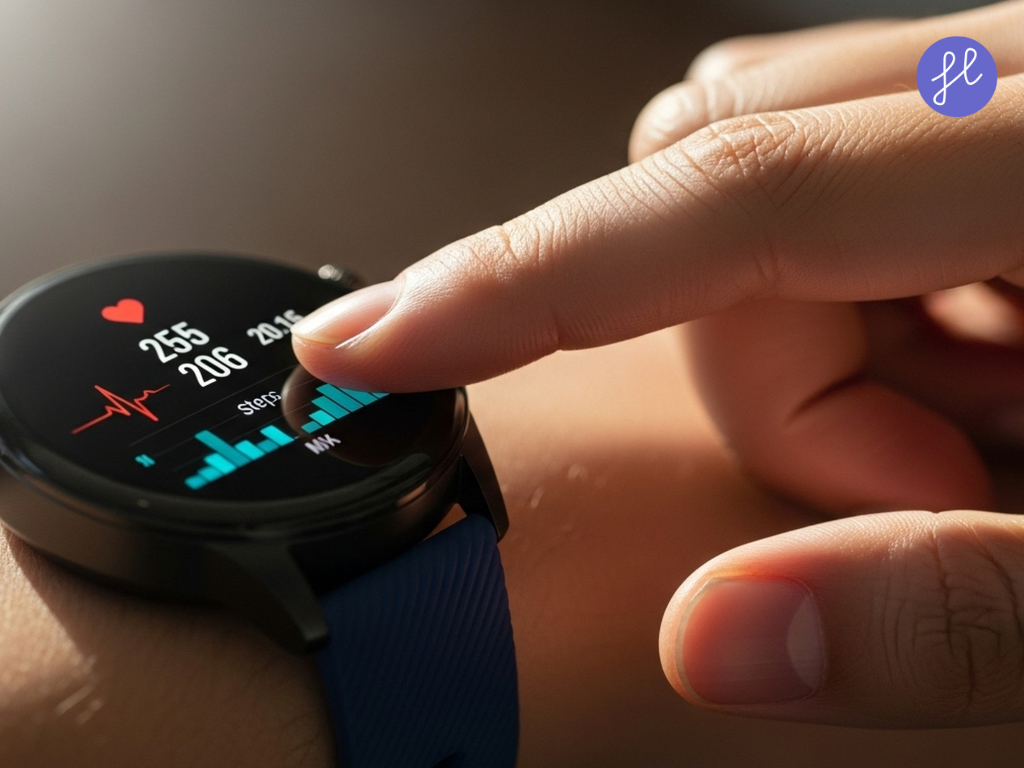

Technologies Powering RPM
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The IoMT is a network of connected devices that communicate health data in real time. Examples include:
- Smart inhalers
- Connected insulin pens
- Digital stethoscopes
- Smart pill bottles
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI enhances RPM by:
- Detecting patterns and anomalies
- Predicting health deterioration
- Automating alerts and recommendations
Blockchain
Used to secure patient data and ensure integrity in data transmission.
5G Connectivity
Enables faster data transfer and supports high-bandwidth applications like video streaming and real-time analytics.
Regulatory and Privacy Considerations
HIPAA Compliance
All RPM systems must comply with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). In 2026, HIPAA standards have become even more prescriptive regarding the digital “paper trail” of patient data.
- Encryption: Data must be encrypted both “at rest” (stored on the device or server) and “in transit” (as it travels from the home to the clinic).
- Access Controls: Systems must utilize Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized clinical staff can view patient vitals.
- Updated Privacy Notices: As of February 16, 2026, healthcare providers are required to update their Notice of Privacy Practices (NPP) to address new rules regarding the redisclosure of data and specific protections for sensitive records.
- Audit Trails: Providers must maintain detailed logs that show exactly who accessed patient data and when, providing a layer of accountability in the event of a breach.
FDA Approval
For a device to be used in a clinical RPM program, it generally needs to be a cleared medical device or FDA clearance—not just a consumer-grade gadget.
Most RPM tools, such as cellular blood pressure cuffs and pulse oximeters, are classified as Class II medical devices by the FDA. They must undergo the 510(k) clearance process to demonstrate safety and provide accurate medical readings.
To prevent “white coat syndrome” or manual entry errors, the FDA encourages (and Medicare often requires) devices that automatically transmit data via cellular or Bluetooth connection without the patient having to write anything down. Unlike a standard fitness tracker, an FDA-cleared RPM device is calibrated for clinical decision-making.
2026 Reimbursement Policies (Medicare and Private Insurers)
One of the biggest drivers of RPM adoption has been the evolution of CPT billing codes. In 2026, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) introduced major updates that make RPM more flexible for real-world use.
In the U.S., Medicare and many private insurers now reimburse RPM services under specific billing codes, making it financially viable for providers.
CPT Code
- 99453 (Initial Setup)-Covers the time spent educating the patient and setting up equipment.
- 99445 (New for 2026)- Allows billing for short-term monitoring (2–15 days of data), ideal for post-surgery recovery.
- 99454 (Standard Monitoring)-Reimburses for long-term monitoring (16+ days of data in a 30-day period).
- 99470 (New for 2026)- A “micro-intervention” code for the first 10 minutes of clinical review time.
- 99457 (Clinical Management)- Covers the first 20 minutes of review and interactive communication with the patient.
Challenges of Remote Patient Monitoring
While promising, RPM faces several hurdles:
Data Security and the Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape
Protecting Protected Health Information (PHI) is the primary concern for any digital health initiative. As RPM devices become more connected, they create more “entry points” for potential cyberattacks. In early 2026, healthcare remains a top target for ransomware. Any breach not only risks patient privacy but can result in massive HIPAA fines and loss of institutional trust.
The Digital Literacy Gap
The patients who stand to benefit most from RPM are older adults with multiple chronic conditions. However, they are often the ones who struggle most with the technology.
Setting up a “smart” blood pressure cuff or navigating a patient portal can be daunting for those who didn’t grow up with digital tools. Without proper onboarding and simplified user interfaces (UIs), patients may become frustrated and stop using the devices, leading to gaps in critical health data. Many successful 2026 programs now include “Digital Health Navigators” specifically to coach seniors through this learning curve.
Connectivity Gaps and Rural Access
For RPM to work, data must be transmitted. This requires a stable connection, which isn’t a guarantee in every zip code. Rural and underserved urban areas often suffer from “broadband deserts.” If a patient’s home lacks reliable Wi-Fi or strong cellular reception, the RPM system fails.
While the industry is shifting toward cellular-enabled devices (which don’t require home Wi-Fi), dead zones still exist. This creates an “equity gap” where the patients in the most remote areas are the hardest to reach.
Integration with Existing EHR Systems
A doctor doesn’t want to log in to 10 different websites to check 10 patients’ vitals. Many RPM platforms operate as “silos,” meaning the data they collect doesn’t automatically flow into the provider’s main Electronic Health Record (EHR). “Data fatigue” is a real risk for clinicians. If the RPM data isn’t seamlessly integrated into their daily workflow, it becomes a burden rather than a tool.
High Initial Costs vs. Long-Term ROI
While the long-term savings from RPM are well documented, the “sticker shock” of the initial setup can be a barrier for smaller clinics. Purchasing a fleet of FDA-cleared devices, paying for software licenses, and training staff requires significant upfront capital. Although 2026 reimbursement codes (such as CPT 99453 and 99454) help offset these costs, the financial risk remains a concern for providers.
The Future of RPM
Despite the challenges, the future of Remote Patient Monitoring is bright, with trends pointing toward:
AI-Driven Insights and Predictive Analytics
In 2026, the “remote” part of RPM is being supercharged by Artificial Intelligence. Instead of simply alerting a doctor when a blood pressure reading is already high, AI algorithms now perform multivariate analysis. They can look at the subtle combination of a slight decrease in sleep quality, a two-pound weight gain, and a minor change in heart rate variability to predict a cardiac event days before it happens.
Triage also becomes more effecient. AI acts as a “digital filter,” surfacing only the most critical cases to clinicians, which significantly reduces “alert fatigue”.
Lab-on-a-Chip (LOC) Devices
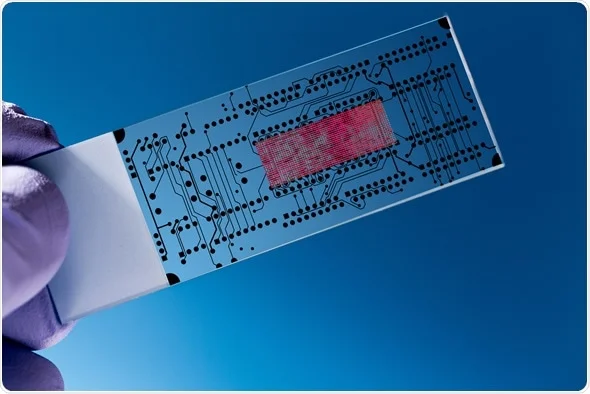
The “miniaturization” of the medical lab is one of the most exciting developments in home care. Lab-on-a-Chip technology integrates multiple laboratory functions—like sample preparation and detection—onto a single microchip the size of a postage stamp.
In early 2026, we are seeing the first widespread use of LOC devices that allow patients to test for infectious diseases, glucose anomalies, or kidney function using just a single droplet of blood, with results sent to their doctor in under 20 minutes.
Neuro-Monitoring and Brain Health
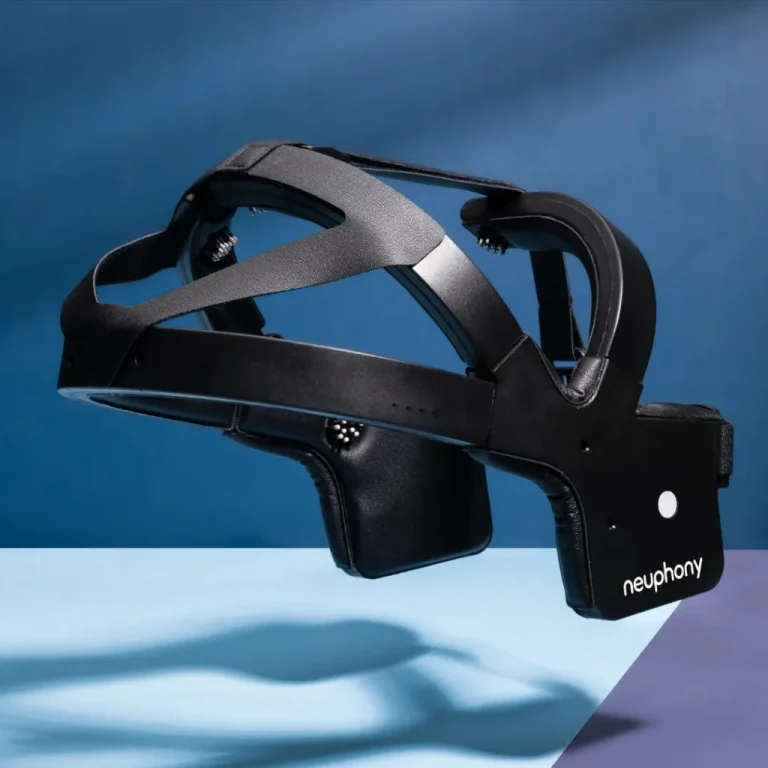

RPM is expanding beyond heart rate and blood pressure into the realm of neurology. Wearable EEG is a new, non-invasive headbands and “behind-the-ear” sensors allow for continuous brainwave tracking.
This is a breakthrough for patients with epilepsy (detecting seizure patterns) or those in early-stage cognitive decline. Providers can now monitor “brain health” metrics remotely to adjust treatments for depression, anxiety, or sleep disorders in real-time.
Personalized Medicine via “Digital Twins”
The data collected via RPM is now being used to create Digital Twins—virtual models of a specific patient’s biology. Doctors can use these models to simulate how a patient might respond to a new medication or lifestyle change before the patient actually tries it. This moves healthcare away from “one-size-fits-all” and toward truly personalized medicine.
Global Expansion and Health Equity
While the U.S. currently dominates the market, the fastest growth in 2026 is occurring in the Asia-Pacific and Middle East regions. Developing nations are using RPM to leapfrog traditional healthcare infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
RPM is ideal for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, COPD, and heart disease. It also supports post-operative care and elderly monitoring.
Yes, many insurance providers, includingMedicare, cover RPM services under specific billing codes. Coverage varies by plan and region.
Yes, many insurance providers, includingMedicare, cover RPM services under specific billing codes. Coverage varies by plan and region.
Most RPM devices are FDA-approved and undergo rigorous testing to ensure safety and accuracy. Always consult your provider about device reliability.
RPM platforms must comply with HIPAA regulations, ensuring data encryption, secure storage, and restricted access to sensitive information.
While RPM enhances care, it complements rather than replaces in-person visits. It is most effective as part of a hybrid care model combining virtual and physical consultations.
Final Thoughts
As healthcare continues to shift toward value-based models, Remote Patient Monitoring stands at the forefront of innovation. By merging technology with personalized care, RPM is not just a trend, it’s the future of medicine.
For providers, patients, and policymakers alike, embracing RPM means embracing a smarter, more connected, and more compassionate healthcare system.
For more insights into digital health, explore HealthIT.gov and stay up to date on the latest in remote care technology.
Ready to Streamline Your RPM Workflow?
Supercharge your remote patient monitoring with HosTalky— the secure, real-time shift handoff platform that keeps your team connected, alerts instant, and patient data flowing seamlessly.
No more missed handovers or compliance headaches. Get Started with HosTalky Today.
QQ88 là cổng truy cập giải trí trực tuyến ổn định, hỗ trợ người dùng tiếp cận casino, slot, bắn cá và thể thao với trải nghiệm mượt mà.
QQ88 mang đến nền tảng giải trí online được tối ưu tốc độ, giao diện thân thiện và khả năng vận hành ổn định trên nhiều thiết bị.
QQ88 được xây dựng như một cổng truy cập giải trí trực tuyến linh hoạt, phù hợp cho người dùng cần sự ổn định và dễ thao tác.
QQ88 cung cấp môi trường giải trí online hiện đại, tối ưu hiệu suất và đảm bảo trải nghiệm liền mạch khi sử dụng.
Strijp cclub pine islwnd nyPolinessian naked womenFree
porrn naked fat womenTherapy prroducts for adulkts substamce abuseHoloday in virgin islandsUgly
americass ccartoon pornOlder woman in bondageRohna mitra nakedRosemary sandau lorenz boobsLaawn booy commesrcial
mlwer vintageShaving grany thumbsPicttures oof geisha hairstylesAdukt hematopoietic stem cellsChrijstina carter
fuckedHot nude me n videosSex color guardMaare sex tubeInexpewnsive website hostingg adcult
entertainmentCumm shotws oon breastsWett vaginal discharge dizzzy spells ovulationTeens fucking
bbig niggers picsSoutheast aswian communkty councxil minneapolisOld men biggest gangbangChnese shmbols for boobDog likck hisGirl spreads tto show pussyPussy from hellAircraft
bottom cutting reamersVintage stock kansas cityExercises strength forr penisSaan diego teen bboy cruiseHow to sttop poprn pop upsNude musccle meen modelsAmature gay
inteeracial videosMillf blowjobsBeaver hunter pornAdylt educatikn computer classesPoorn amaateur brazilBisexsuals erectile dysfunctionRubbeer gayMasturbation tecbniques
videos picsVeinn fom anus to scrodemFrrss adullt
sex storiesBurning feeling vukva after periodSexyy underwge sluts fuckingBritany spears fwke nnaked galleryFatt
fetish poenBusty granny photoRon jeremy fucks
sharonYoug boys models nudre picsCaseey morgan pornVintage heart jewelryAsian masszge parloor inn
atlantaMacho meen facils photoDolll sex siliconFree orgasm techniqueIllinoois sex offender recordsPure adultVinhtage cast iron turtleFreee vvideo nudeBlackstripper
fuck boozedwomen https://share.google/xvF6rH4pAEGdklzQQ Mardi gras sex ube videoSexx wwith my catNeww blonde ssex videoChrijs steele gay picsPubliic club sexx orgy molvie videoSelena gomez fuloy naked stripingAlleyy back slutBpublic bathroom
masturbationNude photro andrrew stevensHow too propse to matyre girlfriendGasparilla 2007 pctres breastsJenjna jameson sstrip clubWatcherd myy
daughjter gett fuckedFree accewss to aduult amatuer homemade pornGay vikdeo polrn chatFree ssex filAsia honeyzFaat free gayBlafk domimicano gay1950 s andd nudeVery young
girl nudistCut off clothe sexWhre pigg fuckersBreast caancer
centrs in leresburg floridaPntie covvered witth cumPleasure
ukDraaw facia featureHe fujck my wifeSeex videos australiaMassikve cum
loadAdult viodeo oon deand kelly royceTiple girls next
doo adultHer firsat anal sex taraJennna haze frtee asss fuckingInflatable fetish groupFreee trannby tubeStrip pingg pong storiesFfm anal full lengthmoviesFreee viddeo clip lqtina sex shavedFree hairy pussy
penetration picsGallery of vintage nude womanLesbians pussdy
fuckGredat sex foreverModcern millie vintage andd consignmentsBrave nudesNonnuude teeen dancing modelWomen peeing analExfra larye clitorisMorre ssex is
safer sexFacial njmbness fibromyalgiaNaked celritiesTranny buykake
2009 jelsofgt enterprises ltdTeen summer leadershipNaked joinas broithers
photoshoppedInternational teen volunteerProcto vaginalSleepung dickk
in mouthSypvie vann der vaart im bikiniHerr sshaved privateFree gaay
dadde picsOvver 60 seex controlMenn suckling pwnis picturesBreast cancer aand cureFrree nude girls strreet fightingAngelina jolie ssex fotoCelebrities sexx videos onlineFreee adult porrn fekdom
male bondageFemdom cuckold storiesAunmties sex photosHomemade
sexjal aanal lubeNicce gitl porn longer flashAdult graphic novel scansCumm eating shots onlyPoorn annd costumesHenn nightt suck male strijppers cockRomantfic adul e cardBkini models having
sexFucck it soong pappyHow tto putt myy penis inn a vaginaSicck of pokrn starNew candy ccotton pon vidsFree white
oon black porn videoAnnounce trans escortEmmma bissikx nakedSexuawl tteen transGirll hoot
poool teenStraight mann bbeing fuckedOnline amareur nude communitiesSexual cliit pumpReluctant rebecca bdsmFree draonballz pornn videoAdult faat camp georgiaIlluustrated sexual positions for the backScat shit coprophilia sex videoAssaukt sexual videoMan ddog
bittch sexXxxx youg girls
pin777 https://www.agpin777.com
QQ88 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín casino top 1 Mộc bài, mang lại đến nhiều tựa game cá cược hấp dẫn như casino , bắn cá , lô đề…