In 2026, the question is no longer “Can AI detect this?” but rather “How quickly can AI help us treat this?” Artificial Intelligence has moved beyond being an experimental tool to becoming the central nervous system of modern medical diagnostics.
Integrating multi-modal data, like combining imaging, genomics, and real-time vitals—AI is providing a level of diagnostic precision that was once science fiction.
This article explores the profound impact of AI in medical diagnostics, examining its applications, benefits, challenges, and the future of intelligent healthcare.
What is AI in Medical Diagnostics?
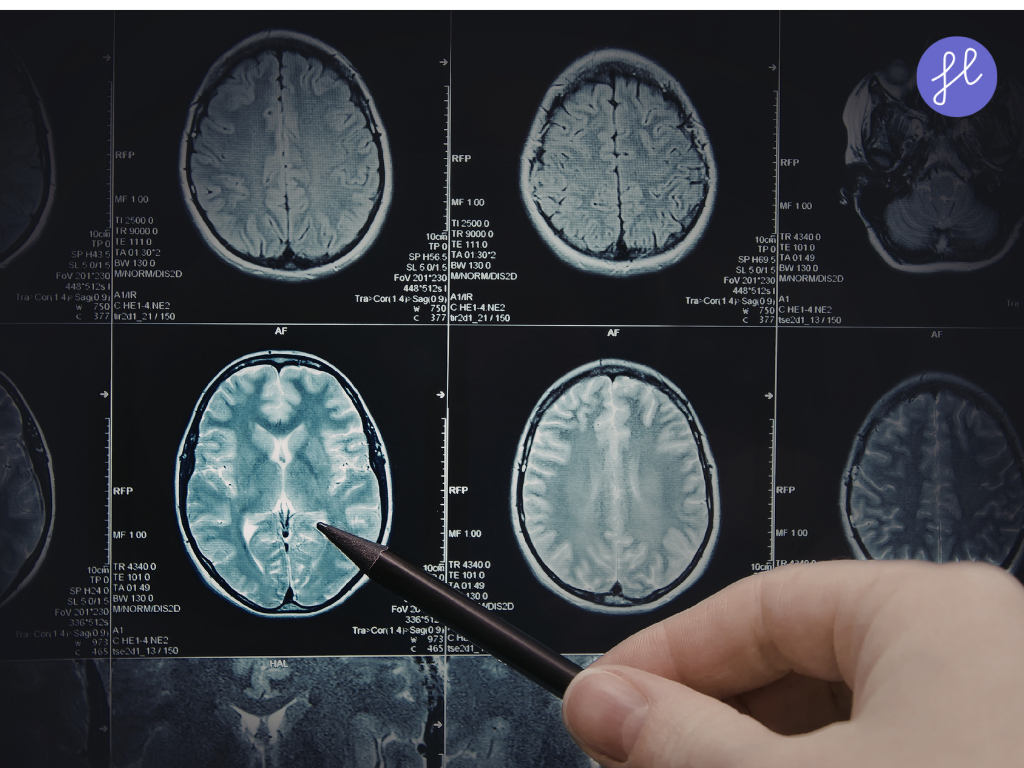
AI in medical diagnostics refers to the use of machine learning algorithms, deep learning, and other AI technologies to analyze complex medical data and assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing diseases. These systems can process vast amounts of information—from imaging scans to genetic data—far faster and more accurately than traditional methods.
Core Technologies Behind AI Diagnostics
- Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms that learn from data and improve over time.
- Deep Learning: Neural networks that mimic the human brain to identify patterns in unstructured data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables machines to understand and interpret medical texts and patient records.
- Computer Vision: Allows AI to interpret visual data like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
How AI is Used in Medical Diagnostics
1. Medical Imaging Analysis
AI excels in interpreting imaging data, often outperforming human radiologists in accuracy and speed. AI algorithms, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), are now the gold standard for “first-pass” screenings.
- Radiology: AI tools now utilize “Radiomics,” turning pixels into data points that measure tumor texture, shape, and volume. This allows for “virtual biopsies” where AI predicts a tumor’s genetic makeup without a physical needle sample.
- Mammography: Systems like MedGemma 1.5 (launched in late 2025) are now used to detect microcalcifications smaller than 0.1mm. These tools prioritize high-risk scans, ensuring a radiologist reviews suspicious cases within minutes.
- Ophthalmology: AI is a “front-line filter” for diabetic retinopathy. In 2026, portable retinal cameras in primary care offices use on-device AI to provide instant “Refer/No Refer” decisions, preventing blindness in underserved areas.
2. Pathology and Histology
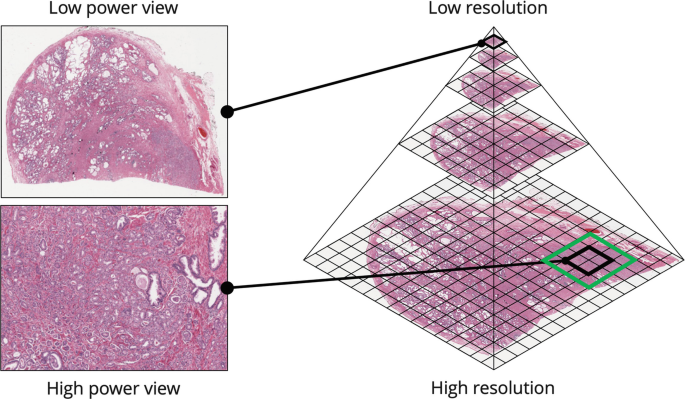
AI systems analyze tissue samples to detect cancerous cells, reducing diagnostic errors and accelerating lab workflows. The traditional glass slide is being replaced by Whole Slide Imaging (WSI).
AI eliminates the “subjective” nature of pathology. Two different systems will now assign the same tumor grade, ensuring consistent treatment regardless of which lab processes the sample. AI can classify brain tumor grades in under 150 seconds during active surgery, allowing surgeons to make immediate decisions.
3. Genomic Data Interpretation
AI processes large-scale genomic data to identify mutations and predict disease risks. AI has solved this. Tools like DeepSEA now predict the effects of “rare mutations” that have never been reported in the clinical literature, identifying whether a mutation is “causal” (disease-causing) or just “noise.”
Targeted Therapies also cross-references a patient’s DNA with a database of millions of clinical trials, and AI suggests the specific “immunotherapy” drug most likely to work for that individual’s genetic profile.
4. Predictive Diagnostics
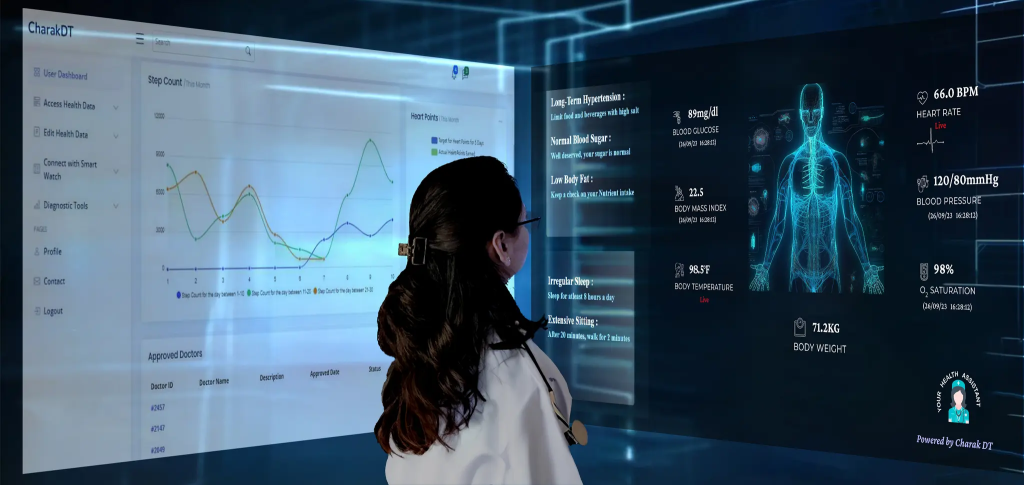
Machine learning models forecast disease progression, hospital readmissions, and potential complications based on patient history and real-time data.
In early 2026, platforms like Charak DT create a “Digital Twin” of a patient’s lungs or heart. Doctors “test” medications on this virtual model to see how they react before giving them to the patient.
Sepsis & ICU Prediction: Machine learning models now monitor real-time hospital data (ECG, blood pressure, oxygen). They can predict the onset of sepsis or cardiac arrest up to 48 hours in advance, giving nurses a critical window for intervention.
5. Clinical Decision Support
AI-powered Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) assist doctors by suggesting diagnoses, recommending tests, and flagging potential issues. AI is particularly adept at spotting “Zebras” (rare conditions). If a patient presents with a rare combination of symptoms across different specialists, the AI links those records to suggest a diagnosis that a single specialist might miss.
Benefits of AI in Medical Diagnostics
Enhanced Accuracy
AI systems act as a rigorous “second set of eyes,” capable of maintaining a level of focus that human clinicians physically cannot sustain over long shifts.
Deep learning models excel at identifying “subtle signals”—patterns in pixels or data points that are nearly invisible to the human eye. For example, AI can detect early-stage lung nodules or minor retinal hemorrhages with up to 98% accuracy. It also eliminates fatigue bias.
Rapid Diagnosis and Improved Clinical Throughput
Time is often the most critical factor in emergency medicine. AI-driven systems process complex datasets in seconds, not hours. In 2026, AI “Agent Studio” platforms automatically flag life-threatening conditions—such as a brain bleed on a CT scan—the moment the image is captured. It also streamlines workflows. By filtering out “normal” results with a 99% Negative Predictive Value (NPV), AI allows specialists to bypass the routine cases.
Operational and Long-Term Cost Efficiency
Predictive analytics can forecast patient deterioration up to 48 hours in advance, allowing for early interventions and reducing readmission, that prevent expensive ICU stays. Ambient Intelligence (such as HosTalky’s AI Scribe) captures patient encounters and automates clinical documentation. This recovers up to 20 hours of clinician time per week. AI also identifies unusual patterns in insurance claims (such as “unbundling” or duplicate billing), potentially saving the global healthcare industry billions annually in fraud prevention.
Precision and Personalized Medicine
With Genomic Integration, AI can analyze a patient’s entire genome to identify specific genetic variants that influence drug efficacy. This enables pharmacogenomics, where doctors prescribe the exact dosage and medication least likely to cause an adverse reaction.
Democratizing Access through Scalability
One of AI’s most profound impacts is its ability to “export” specialist-level expertise to areas that lack specialists. In rural areas where radiologists are scarce, AI-enabled portable ultrasound and X-ray tools can provide immediate screening for conditions like TB or breast cancer.
The Rise of Agentic AI
The newest frontier in 2026 is Agentic AI. While previous generations of AI only “flagged” an issue, Agentic AI coordinates the follow-up:
- Identify: The AI detects a suspicious shadow on a lung scan.
- Orchestrate: It automatically cross-references the patient’s schedule and the hospital’s availability to suggest a biopsy appointment.
- Brief: It synthesizes a “clinical summary” for the specialist, highlighting the exact coordinates and characteristics of the finding.
- Follow-up: It ensures the patient is contacted and that the loop is closed, preventing the “incidental finding” from falling through the cracks.
Real-World Applications of AI in Diagnostics
“Liquid Biopsies” and Multi-Cancer Early Detection (MCED)
AI has revolutionized blood testing. New assays like SPOT-MAS™ use AI to analyze circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in a single 10mL blood draw. In 2026, these tests can identify over 50 types of cancer, often at Stage I or II, when they are most treatable
Digital Twins and Predictive Modeling
Healthcare has shifted from reactive to proactive care through the use of Digital Twins. These are virtual replicas of a patient’s biological systems. Doctors can “test” how a specific tumor might react to a chemotherapy regimen on the digital twin before administering it to the patient. These models learn a patient’s unique “baseline” and can flag a sepsis risk or cardiac event days before physical symptoms appear.
Cardiovascular Disease
AI algorithms detect arrhythmias and predict heart attacks by analyzing ECG data and imaging scans.
Neurological Disorders
AI helps diagnose Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis by analyzing brain imaging and cognitive data.
Infectious Diseases
During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI tools were used to detect pneumonia in chest X-rays and predict patient deterioration.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, AI in diagnostics faces several hurdles:
- Data Quality and Bias: AI systems are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Incomplete or biased datasets can lead to inaccurate diagnoses.
- Regulatory Hurdles: AI tools must comply with stringent FDA and EMA regulations before clinical deployment.
- Cyber-Security: With diagnostic data living in the cloud, medical facilities have become “hardened targets” for hackers, requiring military-grade encryption for every patient file.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Many hospitals struggle to integrate AI with legacy Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems.
- Ethical Concerns: Issues around transparency, accountability, and informed consent must be addressed before widespread adoption.
- The “Human-in-the-Loop” Requirement: Current laws emphasize that AI is a Co-Pilot, not the Captain. A human clinician must still provide the final sign-off on any life-altering diagnosis.
The Future of AI in Medical Diagnostics
Lab-on-a-Chip (LOC)
The next step, already entering pilot phases in late 2026, is the Lab-on-a-Chip. This technology will allow patients to perform complex diagnostic tests—previously performed in hospital labs—using a single drop of blood and a smartphone attachment.
Explainable AI (XAI)
Future AI systems will provide transparent reasoning behind their diagnoses, increasing trust among clinicians and patients.
AI-Powered Wearables
Devices like smartwatches and biosensors will continuously monitor vital signs and alert users to potential health issues.
Federated Learning
This approach allows AI models to learn from decentralized data sources without compromising patient privacy.
AI and Robotics
Integration with surgical robots will enable real-time diagnostic feedback during procedures.
Final Thoughts
The integration of AI in medical diagnostics marks a paradigm shift in healthcare. By augmenting human expertise with intelligent algorithms, we are entering an era where diseases can be detected earlier, treatments can be more personalized, and healthcare can be more accessible and efficient. As technology continues to evolve, so too will our ability to diagnose and treat with unprecedented precision.
To stay updated on the latest in AI healthcare innovations, explore resources like NIH’s AI initiatives and Nature’s AI in Medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
AI can match or even surpass human experts in diagnosing certain conditions, especially in medical imaging and pathology. However, it is most effective when used as a support tool alongside clinical judgment.
No. AI is designed to assist, not replace, healthcare professionals. It enhances decision-making and reduces workload, allowing doctors to focus on patient care.
Risks include data bias, misdiagnosis due to poor training data, and lack of transparency in decision-making. Regulatory oversight and ethical frameworks are essential to mitigate these risks.
Yes, several AI tools have received FDA approval, including those for radiology, ophthalmology, and pathology.
AI platforms must comply withHIPAA and other data protection laws. Techniques like encryption and federated learning help safeguard patient privacy
QQ88 trang 1 google.com.vn
QQ88 LÀ NHÀ CÁI CƯỢC UY TÍN SỐ 1 VN
ình vào bằng Link fly88 thấy ổn định, không bị lỗi chuyển hướng.
ình vào bằng Link fly88 thấy ổn định, không bị lỗi chuyển hướng.
Hello! I just would like to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you have here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.