Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept in healthcare—it’s a reality that’s reshaping how we diagnose, treat, and care for patients.
From predictive analytics to robot-assisted surgeries, AI is driving unprecedented innovation and efficiency, offering solutions that were once considered impossible.

The sheer speed and scale at which AI is transforming healthcare are nothing short of remarkable.
As the global healthcare landscape faces growing challenges like an aging population, rising costs, and the need for personalized care, AI stands at the forefront as the key to unlocking a future of improved outcomes and reduced costs.
The statistics presented here aren’t just numbers—they’re a glimpse into the future of medicine, where AI could save billions of dollars, reduce hospital admissions by half, and even predict disease outcomes with precision previously unimaginable.
Read also: What is Generative AI in Healthcare and How is it Used
AI’s Explosive Market Growth in Healthcare
The AI healthcare market is growing at an unprecedented pace, driven by the demand for improved efficiency and patient outcomes.
- The global AI in healthcare market is expected to reach $188 billion by 2030, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 37% from 2022 to 2030.
- The market was valued at $22.45 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $88.26 billion by 2028.
- In the U.S., AI has captured 58% of the global healthcare market share, while the Asia-Pacific region holds 40.9%.
- North America is currently the dominant player in AI for healthcare, with a market share of 59.1%.
AI’s Impact on Healthcare Costs and Efficiency
AI is improving healthcare by reducing costs and improving operational efficiencies across various applications.
- AI has the potential to reduce the cost of drug discovery by up to 70%. The AI-driven drug discovery market alone is expected to reach $12.8 billion by 2032.
- By 2026, AI is projected to save the U.S. healthcare system $150 billion annually, thanks to more efficient diagnostics, patient management, and administrative workflows.
- AI-assisted surgery could reduce complications and hospital stays by more than 20%, translating into annual savings of $40 billion.
- AI applications in healthcare could help cut U.S. healthcare spending by 5-10%, which equates to a reduction of between $200 billion and $360 billion annually.
Also read Pros and Cons of AI in Healthcare| Truth Revealed

Key Applications of AI in Clinical Settings
AI’s most promising impact lies in its clinical applications, ranging from diagnostics to surgical assistance.
- AI-powered diagnostics tools are widely adopted in the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), with 34% of AI applications used for diagnostics like image analysis, pathology, and endoscopy.
- In the U.S., AI tools helped Moderna optimize its COVID-19 vaccine development using an AI model trained on 20,000 mRNA sequences, significantly accelerating the time to market.
- AI can now predict cancer patient survival rates with 80% accuracy based on oncologist notes and patient data.
- By the end of 2023, AI stroke diagnosis tools will be available in 100% of stroke centers in the UK, helping to speed up detection and treatment.
AI’s Role in Administrative Efficiency
AI is transforming clinical settings and optimizing healthcare administration, allowing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
- Physicians who use AI technologies report a 20% increase in time spent on patient care, as administrative tasks are handled more efficiently by AI-powered systems.
- AI chatbots, such as Sensely’s “Molly,” are expected to save the healthcare industry $20 billion annually by automating patient triage and symptom analysis.
- In 2023, 90% of large healthcare organizations have an AI and automation strategy in place, up from 53% in 2019.
AI’s Role in Healthcare Professionals
Healthcare professionals are embracing AI, particularly for its ability to enhance clinical efficiency and improve patient outcomes.
- A survey of 1,081 physicians found that 63% of respondents believe AI will significantly reduce the time spent on documentation and administrative tasks.
- Among European radiologists, 75.7% consider AI-based algorithms reliable for assisting in patient diagnoses.
- More than 50% of healthcare professionals in Europe and North America believe that AI will be integral to clinical decision-making in the next 10 years.
AI’s Role in Precision Medicine and Personalized Care
AI is playing a crucial role in advancing precision medicine, helping healthcare providers tailor treatments to individual patients based on their unique characteristics.
- The precision medicine market powered by AI is expected to reach $14.5 billion by 2030, focusing on oncology and neurology.
- AI-driven precision medicine tools could reduce medication dosing errors by as much as $16 billion annually.
- AI can predict cancer patient survival with 80% accuracy, allowing healthcare providers to make more informed treatment decisions.
AI’s Role in Drug Discovery
The integration of AI in drug discovery is proving to be one of its most promising applications, saving both time and costs in the development of new medications.
- The global drug discovery market, fueled by AI, is expected to reach $133.11 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 9.2% from 2023 to 2032.
- AI has the potential to reduce the cost of discovering new drugs by up to 70%, significantly speeding up research and clinical trials.
- Moderna’s success in rapidly developing its COVID-19 vaccine was largely attributed to AI, which helped design and test the vaccine in just 42 days by analyzing 20,000 unique mRNA sequences.
AI is now a vital tool in identifying drug candidates and repurposing existing drugs, helping to accelerate the delivery of lifesaving treatments to patients.
AI’s Role in Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
AI’s ability to analyze complex medical images is revolutionizing the way we diagnose diseases, providing faster and more accurate results.
- AI is used in 34% of medical diagnostic applications within the NHS, particularly in imaging analysis for conditions such as lung cancer and stroke diagnosis.
- The AI medical imaging market alone is projected to grow at a CAGR of 26.5% from 2021 to 2028, reaching billions in value.
- In a major advancement, AI-assisted robotics in surgeries is expected to save hospitals $40 billion annually by 2026 by reducing surgical complications and hospital stays.
AI-based algorithms are not just faster—they are consistently more accurate.
For example, AI can detect early signs of dementia with 90% accuracy, comparable to traditional methods.
AI’s Role in Patient Engagement
AI-driven solutions are enhancing patient engagement by providing personalized care and improving communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- By 2026, AI virtual nursing assistants are expected to reduce patient maintenance tasks by 20%, saving the healthcare industry $20 billion annually.
- AI-powered chatbots are becoming an integral part of healthcare, helping patients manage symptoms and medication schedules, with 53% of healthcare providers in Asia Pacific and South America expecting chatbots to play a major role in patient care by 2031.
- 65% of U.S. adults have expressed interest in AI being used for their skin cancer screenings, showing growing confidence in AI’s potential to improve diagnostic accuracy .
These AI-driven tools are especially valuable in addressing healthcare labor shortages and improving patient satisfaction by offering more accessible, real-time care.
AI’s Role in Reducing Racial and Ethnic Bias
One of AI’s most promising societal impacts is its ability to reduce human biases, particularly in the healthcare sector, where disparities in treatment based on race and ethnicity have been long-standing issues.
- In the U.S., 51% of adults who recognize racial bias in healthcare believe that AI can help level the playing field by offering more objective, data-driven decisions.
- AI’s neutrality in data processing and decision-making has been highlighted as a key factor in eliminating biases, with 36% of surveyed individuals noting that AI doesn’t discriminate based on appearance or race.
As AI continues to evolve, healthcare providers are looking to leverage its potential for fostering equity in healthcare, especially for underserved populations.
Ethical and Privacy Concerns Surrounding AI
While the benefits of AI in healthcare are substantial, ethical and privacy concerns remain a barrier to widespread adoption.
- 60% of Americans are uncomfortable with their healthcare provider relying on AI for diagnosing conditions, primarily due to concerns about privacy and the security of their medical records.
- Additionally, 57% of adults in the U.S. worry that AI might weaken the relationship between patients and physicians, emphasizing the need for transparency and human oversight in AI-driven decision-making.
- To ensure ethical deployment, organizations like the American Medical Association (AMA) are pushing for AI to be designed and used in a manner that is equitable, responsible, and transparent.
- 75% of Americans believe that the healthcare industry will implement AI too quickly without fully understanding its risks.
- Despite concerns, 65% of Americans would prefer AI to be used in their skin cancer screenings, with 55% believing it could improve diagnostic accuracy.
Healthcare providers and AI developers must address these concerns by enhancing AI’s transparency and ensuring that human oversight remains an integral part of AI-driven healthcare solutions.
AI In Healthcare: Study Metrics
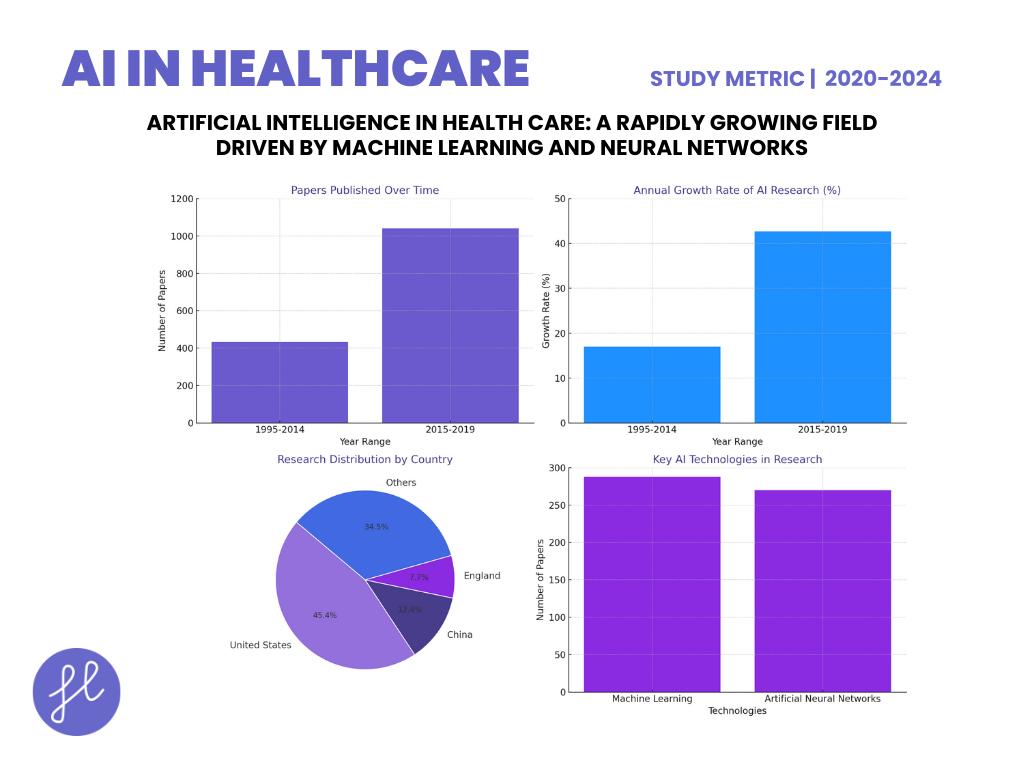
- The bibliometric study by Guo et al. (2020) provides an in-depth analysis of the rapid growth of AI research in health care from 1995 to 2019.
- The study reveals an average annual growth rate of 17.02%, with an even steeper rise of 42.67% between 2015 and 2019, during which 70.67% of the total 1,473 papers were published.
- Geographically, 95.59% of the research comes from 10 countries, with the United States leading at 45.42%, followed by China (12.42%) and England (7.67%).
- Key AI technologies used include machine learning (featured in 288 papers) and artificial neural networks (270 papers), with cancer being the top health issue addressed (273 mentions).
- Research hotspots include cancer, convolutional neural networks, and tumor markers, with predominant research domains in computer science (252 publications), engineering (192), and medical informatics (169).
- The study underscores the need to bridge the gap between AI research and clinical practice, as AI shows great promise in improving diagnosis and disease management.
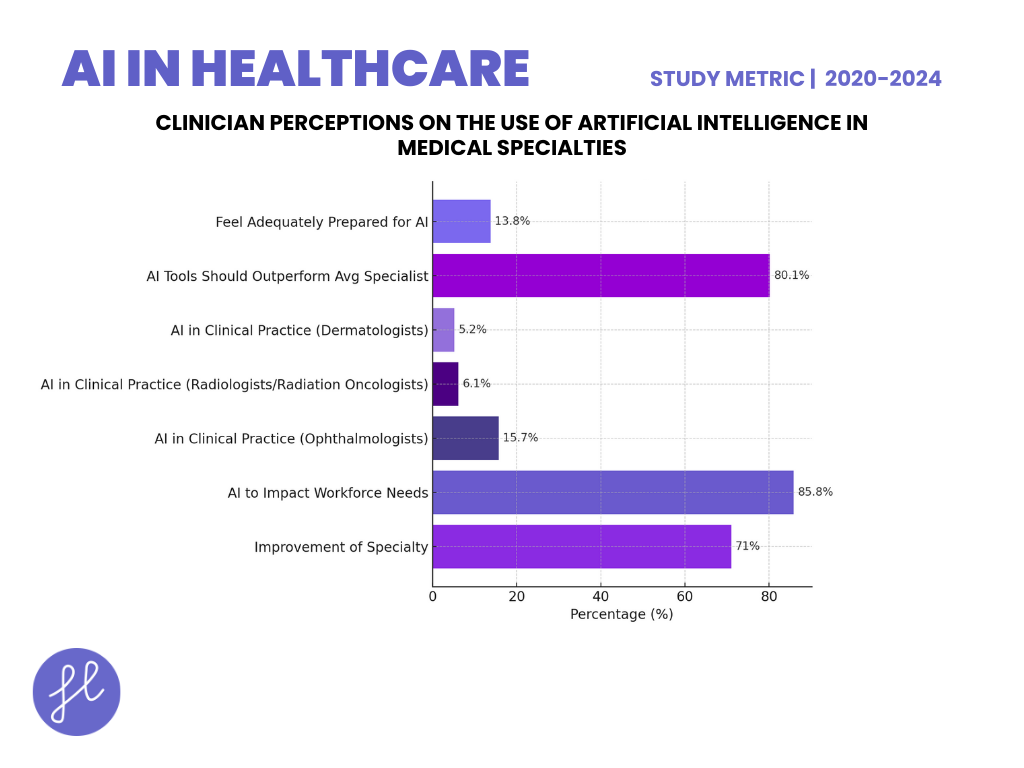
Clinician Perceptions on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Specialties
- In a 2021 study by Scheetz et al., a survey was conducted among 632 clinicians from Australia and New Zealand specializing in ophthalmology, dermatology, radiology, and radiation oncology to assess their views on artificial intelligence (AI) in their fields.
- The majority (71%) of respondents believed AI would improve their specialty, with 85.8% expecting AI to impact workforce needs within the next decade. The survey revealed differences in AI usage, with 15.7% of ophthalmologists using AI in clinical practice compared to just 6.1% of radiologists/radiation oncologists and 5.2% of dermatologists.
- Respondents also had high-performance expectations for AI, with 80.1% believing AI tools for diagnostic decision support should outperform the average specialist.
- While AI was generally seen as beneficial, concerns included the divestment of healthcare to technology companies and medical liability due to machine error. Education on AI was identified as a critical need, with only 13.8% of respondents feeling adequately prepared for AI integration.
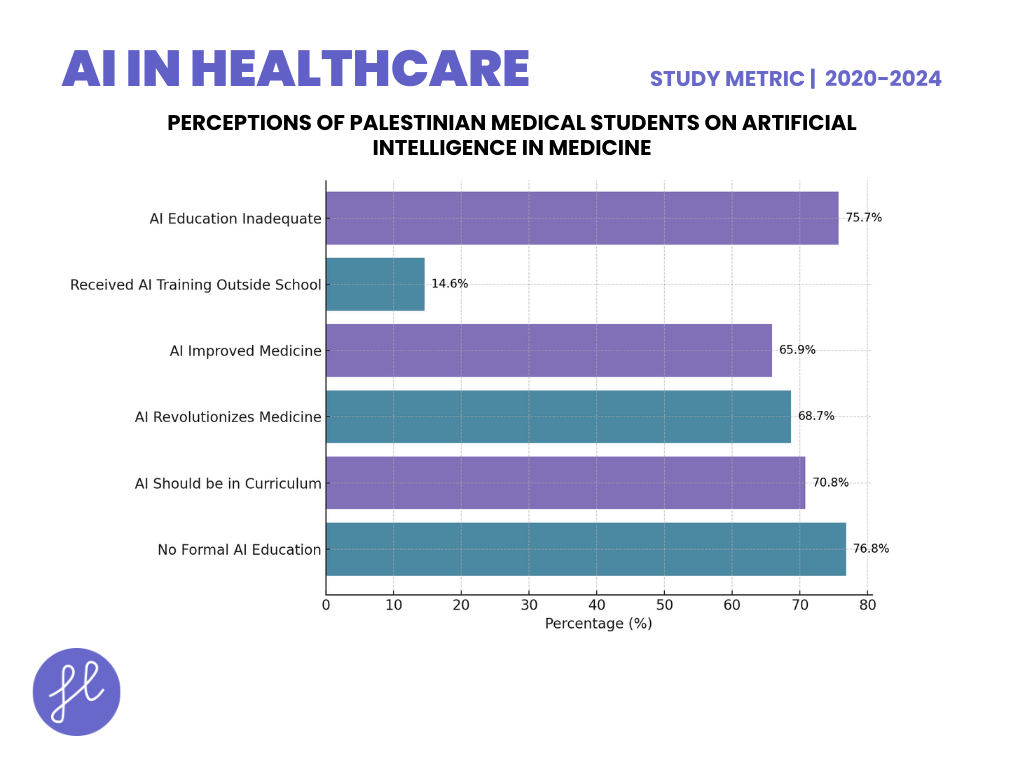
Perceptions of Palestinian Medical Students on Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
- A recent 2024 mixed-methods study by Jebreen et al. explored the attitudes of 349 Palestinian undergraduate medical students toward artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine.
- The study revealed that 76.79% of participants had not received formal education on AI before or during medical school, and 70.8% believed AI should be incorporated into medical curricula.
- Most students (68.7%) agreed that AI would revolutionize medicine, and 65.9% felt it had already improved the field. However, only 14.6% had received training on AI outside formal education.
- Male students had higher perception scores than females (3.15 vs. 2.81, p < 0.001), indicating gender differences in AI readiness. Students emphasized the importance of learning opportunities, with 75.7% considering AI education inadequate, suggesting a strong need for formal AI training in Palestinian medical education.
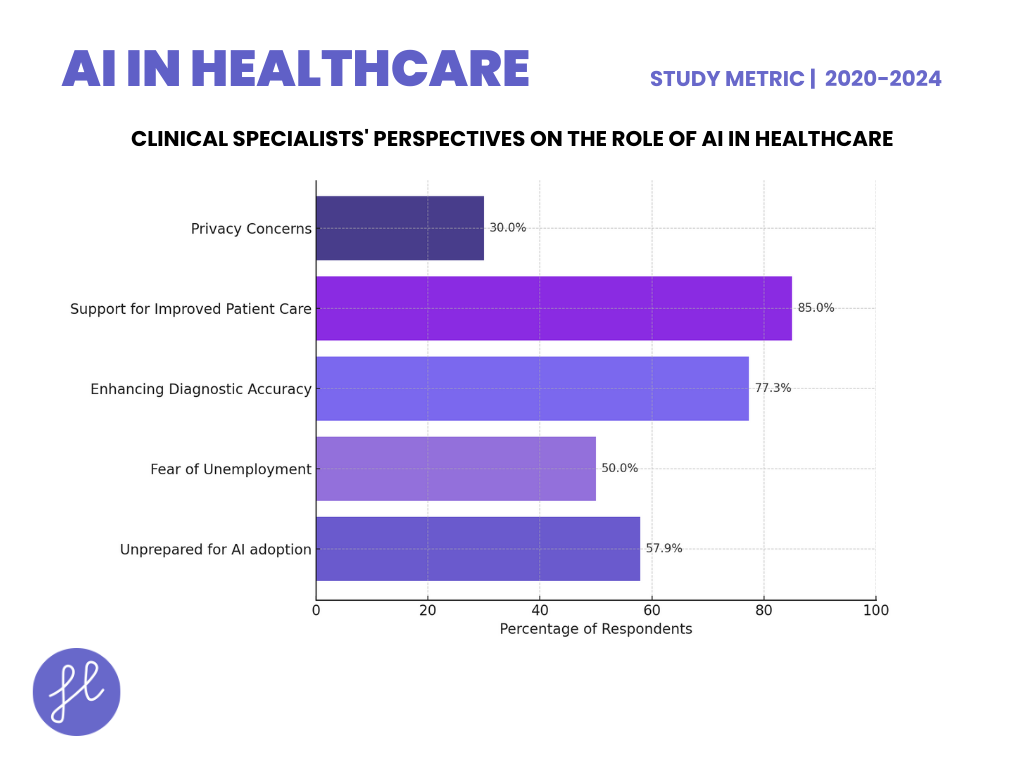
Clinical Specialists’ Perspectives on the Role of AI in Healthcare
- A 2024 study by Daniyal et al. examined the opinions of 140 clinical specialists from Southern Punjab, Pakistan, regarding AI’s future in healthcare.
- Results revealed that 57.9% believed hospitals were unprepared for AI adoption, while 50% feared AI could lead to unemployment. However, 77.3% agreed AI could enhance diagnostic accuracy, and 85% supported its potential to improve patient care through data automation.
- Specialists with less experience were more open to AI adoption (p = 0.0327, OR = 3.184), while privacy concerns were prominent, with 30% fearing data violations. This study underscores the need for AI training and policy development in healthcare.
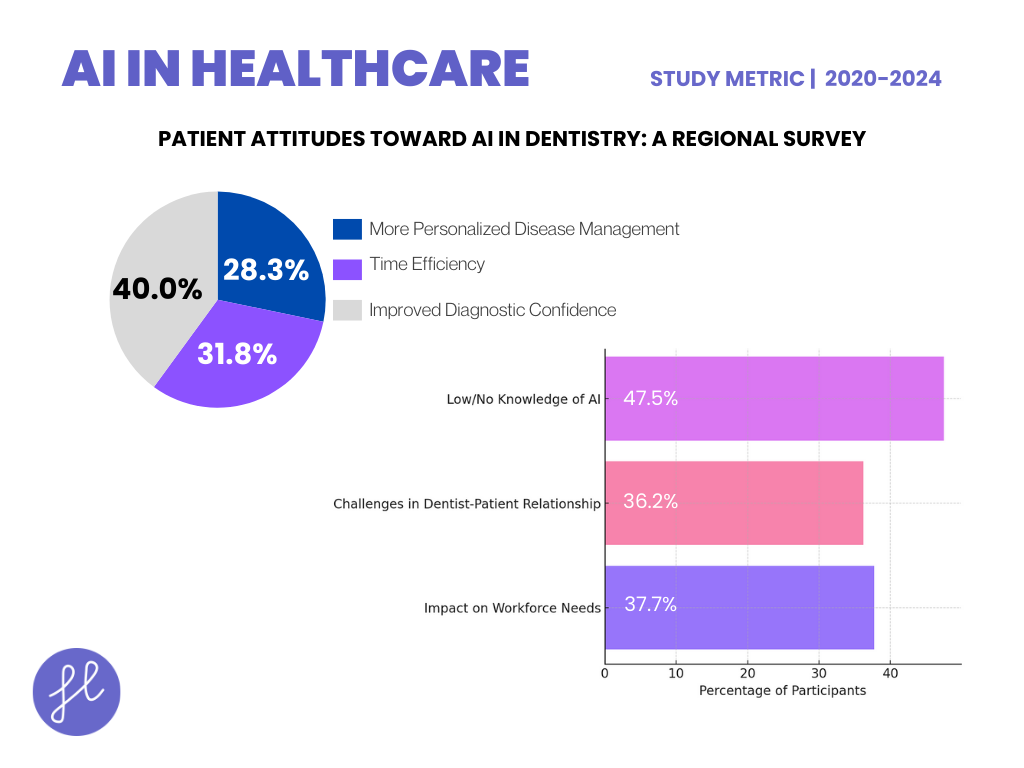
Patient Attitudes Toward AI in Dentistry: A Regional Survey
- A 2023 study by Ayad et al. explored patient perceptions of AI in dentistry, gathering responses from 265 participants.
- The top perceived advantages of AI were improved diagnostic confidence (60.8%), time efficiency (48.3%), and more personalized disease management (43.0%).
- On the downside, 37.7% worried about its impact on workforce needs, while 36.2% cited potential challenges in the dentist-patient relationship. Notably, 47.5% of participants reported low or no knowledge of AI, and most expected AI to become integrated into dental workflows within 1–10 years.
- Despite concerns, overall patient attitudes were positive, with many seeing AI as a beneficial addition to dental care.
The Future of AI in Healthcare is here!
Looking forward, AI’s influence on healthcare will only continue to grow as its applications expand and new technologies emerge.
- AI is projected to dominate future healthcare systems, with robot-assisted surgeries expected to generate $40 billion in revenue by 2026 .
- By 2030, AI-based healthcare systems will be critical in 90% of hospitals worldwide, transforming early diagnosis and remote patient care.
AI-driven tools could reduce hospital admissions by 50%, leading to better resource allocation and patient care.
More on AI in Healthcare here : 15 Ways AI is Being Used in Healthcare
The Future of Healthcare is Powered by AI
The data speaks for itself—AI is revolutionizing healthcare in ways that are not only impactful but transformative.
From saving billions in healthcare costs to improving the accuracy of diagnostics and personalizing treatment plans, AI is no longer an optional innovation; it’s a necessity.
However, as healthcare integrates more AI technologies, it’s crucial to address public concerns about privacy, transparency, and the patient-provider relationship.
The potential is limitless, but it must be harnessed with responsibility. As we look to the future, AI will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in healthcare, paving the way for smarter, faster, and more effective care.
The future of healthcare is here, and AI is leading the charge.
Join HosTalky on LinkedIn and be a part of the healthcare communication revolution! 🌟
With our productivity-enhancing tools, we’re transforming how healthcare professionals connect, collaborate, and streamline work. Whether you’re a healthcare provider, administrator, or industry professional, HosTalky offers innovative solutions to make your day-to-day tasks easier and more efficient.
Follow us for the latest updates, industry insights, and tips! Let’s elevate healthcare together!
👉 Stay connected with HosTalky on LinkedIn: HosTalky on LinkedIn
