Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing healthcare quickly, offering better patient care, more accurate diagnoses, and improved efficiency. But a big question remains: Can we really trust AI in healthcare?
This article looks at the facts, clears up common myths, and shares insights on AI’s current and future role in healthcare.
TLDR: Can AI Be Trusted in Healthcare?
- AI in Healthcare Growth: The global AI healthcare market is projected to grow from $26.69B in 2024 to $613.81B by 2034, with a CAGR of 38.5%.
- Current Adoption: 18.7% of US hospitals use AI; primary applications include optimizing workflows, automating tasks, and predicting patient demand.
- FDA Approvals: As of 2023, 692 AI-enabled medical devices have been approved, with radiology making up 77% of these approvals.
- Diagnostic Accuracy: AI shows impressive performance in radiology (94%), breast cancer screening (97%), and ECG analysis (85.7% accuracy).
- Misconceptions: AI will not replace doctors, is not infallible, and has limitations like biased training data and complex implementation.
- IBM Watson Case Study: IBM Watson faced failure due to insufficient data, overselling capabilities, and high costs.
- FDA Device Recalls: 4.8% of FDA-approved AI devices have been recalled, highlighting the need for better safety tracking.
- Trust Factors: Trust in AI is affected by transparency, technical limitations, and healthcare culture.
- Future AI Trends: Trends include AI-assisted medical assistance, intelligent clinical coding, and improved regulatory frameworks.
- Building Trust: To trust AI, healthcare institutions need robust governance, transparency, diverse data, and human-centered design.
- HosTalky’s Role: Helps with communication, change management, and workforce development to support AI integration in healthcare.
The Current State of AI in Healthcare

The AI healthcare industry has experienced unprecedented growth, with the global market valued at $26.69 billion in 2024 and projected to reach $613.81 billion by 2034, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.5%.
Current adoption rates reveal a mixed landscape across healthcare institutions. The primary applications include:
- Optimizing workflow (12.91%)
- Automating routine tasks (11.99%)
- Predicting patient demand (9.71%)
- Managing staffing needs.
The regulatory environment has also evolved rapidly to accommodate AI innovations. As of 2023, the FDA has approved 692 AI-enabled medical devices, with radiology accounting for 77% of these approvals. This represents a significant increase from just 6 approved devices in 2015.
Geographic Distribution and Leading Institutions
Healthcare AI adoption varies significantly by region. Internationally, research institutions are making substantial contributions, with Mount Sinai Health System ranking as the top healthcare institution according to the Nature AI Index 2024.
Key AI in Healthcare Applications and Their Effectiveness
Diagnostic Accuracy: Facts vs. Expectations
AI’s diagnostic capabilities have shown remarkable promise in various medical specialties. Recent studies demonstrate impressive performance metrics across different applications:
- Radiology and Medical Imaging: AI algorithms have achieved 94% accuracy in early disease detection, particularly in tumor identification from patient scans, surpassing the performance of professional radiologists in specific contexts 6. In breast cancer screening, AI systems have achieved 97% accuracy in predicting breast cancer risk from mammograms.
- Cardiovascular Applications: AI-powered ECG analysis has demonstrated significant clinical utility, with one study showing 85.7% accuracy, 86.3% sensitivity, and 85.7% specificity when tested on over 52,000 patients for detecting ventricular dysfunction. Another AI system achieved a 98.51% recognition rate and 92% testing accuracy in diagnosing ECG arrhythmias.
- Ophthalmology: The collaboration between Moorfields Eye Hospital and DeepMind resulted in an AI tool capable of identifying more than 50 eye diseases with 94% accuracy, matching the diagnostic capabilities of top eye professionals.
However, a detailed review of generative AI’s diagnostic abilities only showed 52.1%. This performance was similar to that of non-expert doctors but much lower than that of expert physicians.
Specialized Medical Applications
- Precision Medicine: AI is particularly effective in creating personalized treatment plans. For example, researchers developed a system that accurately identified 92% of kidney structures in 1,819 samples, with only 10.4% false positives.
- Surgical Applications: AI-assisted robotic surgery is improving precision and outcomes. These systems guide surgeons in real-time, automate specific tasks, and enable minimally invasive procedures, giving doctors more control and flexibility.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI is speeding up drug research by analyzing large amounts of data to find potential drug candidates and improve clinical trials.
The Trust Equation in Healthcare AI
This is where things get a little complicated. Recent studies show that 92% of healthcare leaders believe generative AI helps improve efficiency, while 65% see it as a way to make faster decisions.
However, several challenges affect trust:
Individual Characteristics
Research indicates that vulnerable groups—such as less educated individuals, the unemployed, immigrants from non-Western countries, older adults, and patients with chronic conditions—tend to trust AI less. This highlights the need to address fairness and accessibility in AI use.
Technical Transparency
Many AI systems are like “black boxes,” meaning their workings are not clear. This lack of transparency makes it hard for healthcare providers to trust them. Clinicians need AI systems that can explain their recommendations clearly.
Healthcare Culture and Governance
Trust is shaped by the culture within healthcare, which encompasses factors such as medical specialties, task complexity, and the views of respected colleagues. That is why strong governance, including clear policies and guidelines, is essential for building and maintaining trust in AI systems.
Common Misconceptions About Healthcare AI
With still a number of doubts, so do the common myths about the application of AI in healthcare.
Misconception 1: AI Will Replace Healthcare Professionals
One of the most persistent myths is that AI will replace doctors and nurses/ The reality is that AI is designed to augment and enhance human capabilities rather than replace them. Healthcare professionals bring empathy, holistic judgment, and nuanced communication that AI cannot replicate.
Misconception 2: AI is Objective and Infallible
Many assume that AI’s computational capacity makes it perfect and impartial. However, AI systems inherit biases from their training data and can make errors ranging from misdiagnoses to misread images in suboptimal conditions.
Misconception 3: Implementation is Simple and Quick
Healthcare organizations often underestimate the complexity of AI implementation. Successful integration requires extensive testing in clinical settings, workflow customization, cultural integration, and ongoing training and change management.
Misconception 4: High Accuracy Equals Better Outcomes
While accuracy statistics are essential, they don’t automatically translate to improved efficiency or patient outcomes. Real effectiveness requires optimization of entire workflows, not just individual tasks.
What We Can Learn from the IBM Watson Case Study
The story of IBM Watson for Oncology offers valuable lessons about the challenges of implementing AI in healthcare. Despite IBM’s $4 billion investment and ambitious promises, Watson Health was ultimately sold off in parts in 2022.
Key factors contributing to Watson’s failure included:
- Insufficient Data: Doctors reported that there wasn’t enough quality data for the program to make reliable recommendations.
- Overselling Capabilities: IBM’s marketing created unrealistic expectations about Watson’s capabilities.
- Implementation Challenges: The system struggled with the real-world complexity of clinical settings and the integration of workflows.
- High Costs and Regulatory Hurdles: The high costs of development and maintenance, combined with privacy concerns and regulatory compliance requirements, hindered adoption.
FDA Device Recalls and Safety Issues
Adding to the challenges associated with the use of AI in healthcare technology are FDA recalls on some AI-powered healthcare devices.
Even with strict approval processes, recent data shows that 43 out of 903 FDA-approved AI devices (4.8%) have been recalled, with an average of 1.2 years between approval and recall.
An analysis of 429 safety reports related to AI medical devices found that 108 (25.2%) were possibly linked to AI, while 148 (34.5%) lacked enough information to assess AI’s role. This highlights the need for enhanced reporting and tracking systems to address safety issues related to AI.
Governance and Risk Management
The 2025 ECRI Top 10 Patient Safety Concerns report identified “Insufficient Governance of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare” as the second most critical patient safety concern. The report found that only 16% of hospitals have comprehensive AI governance policies, despite the rapid adoption of AI technologies in healthcare.
Effective AI governance should focus on several key areas:
- Bias Recognition and Mitigation: Identifying and reducing bias throughout the entire AI model lifecycle.
- Data Privacy and Security: Establishing strong frameworks to protect patient data and comply with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR.
- Clinical Validation: Conducting thorough testing and validation of AI systems in real-world clinical settings.
- Human Oversight: Ensuring adequate human supervision and decision-making authority in the use of AI systems.
Emerging Trends and Applications of Generative AI in Healthcare
Generative AI in healthcare is a rapidly growing segment of healthcare AI, with the market projected to reach $21 billion by 2032.
Key applications include:
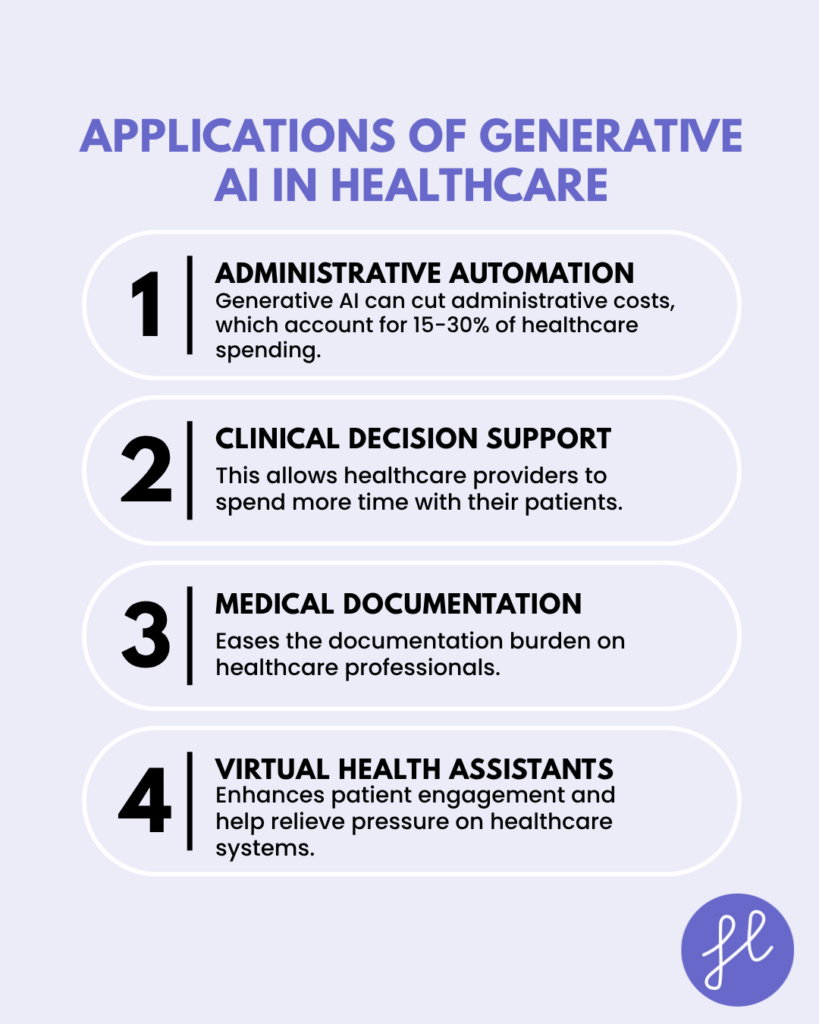
Administrative Automation
Generative AI helps streamline administrative tasks such as scheduling patient appointments, managing medical records, and processing claims. These applications can cut administrative costs, which account for 15-30% of healthcare spending.
Clinical Decision Support
AI systems like IBM Micromedex with Watson are speeding up clinical searches, reducing the time from 3-4 minutes to under 1 minute. This allows healthcare providers to spend more time with their patients.
Medical Documentation
Ambient listening technologies are changing clinical documentation by automatically turning patient-provider conversations into clinical notes, which eases the documentation burden on healthcare professionals.
Virtual Health Assistants
AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots offer 24/7 patient support, help with symptom checking, and monitor medication adherence. These systems enhance patient engagement and help relieve pressure on healthcare systems.
Read more on 10 Powerful Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare
2025 Healthcare AI Trends
Several key trends are shaping the future of AI in healthcare:
- Agentic Medical Assistance: These systems can interact with multiple healthcare systems, analyze patient data, and facilitate care coordination.
- Intelligent Clinical Coding: Advanced AI systems are automating medical coding processes, improving accuracy and reducing administrative burden. Enhanced
- Integration and Interoperability: AI solutions are becoming more sophisticated in their ability to integrate with existing healthcare systems and workflows.
- Regulatory Evolution: The FDA and other regulatory bodies are developing more sophisticated frameworks for the approval of AI devices and post-market surveillance.
So, How Can We Build Trustworthy AI Systems?
Let’s start by discussing evidence-based recommendations:
- Organizations should develop comprehensive AI governance policies that focus on reducing bias, protecting data privacy, validating clinical applications.
- AI systems need to provide clear explanations for their recommendations to foster trust among healthcare providers and patients.
- Training datasets must reflect the diversity of the populations being served to minimize bias.
- AI should support, not replace, human judgment, preserving essential aspects of healthcare like empathy, communication, and personalized care.
- Ongoing surveillance systems should be in place to identify and address AI-related safety issues.
How HosTalky Can Help
HosTalky offers a platform designed to enhance communication among healthcare staff, which can support these implementation challenges:
- Change Management: Simplifies collaboration and helps staff adapt to new AI systems with ease.
- Interoperability: Integrates smoothly across devices, ensuring that all team members stay connected and informed, regardless of their location or platform.
- Workforce Development: With features like AI-powered text assistance and secure note-taking, HosTalky can facilitate training and support staff in developing essential AI skills.
- HIPAA Compliance: HosTalky is HIPAA compliant, so patient data is handled securely and appropriately, which is crucial for maintaining trust and compliance in healthcare settings.
Final Thoughts
The question of whether AI can be trusted in healthcare requires a thoughtful, evidence-based approach. Current research indicates that AI has significant potential to improve healthcare outcomes, particularly in areas such as medical imaging, diagnostic support, and administrative tasks.
However, real-world implementation faces challenges such as data quality issues, bias, and integration problems.
AI can be trusted in healthcare when implemented with appropriate safeguards and realistic expectations. As generative AI and other technologies advance, tools like HosTalky will be vital in addressing communication and facilitating powerful partnerships between AI and human expertise.
📲 Want more insights on the healthcare workplace and technology? Follow us on LinkedIn & Instagram!

Goood article. I will bbe going throuvh manyy of thse issues as
well..
G’day, mates! au88bet popped up on my radar. I’m always keen for a good Aussie-themed betting site. Looks promising, haven’t placed any bets *yet*, but the odds look competitive. Thoughts? Give it a burl: au88bet
SVV388211, now that’s a mouthful! Wonder what makes them different from the original SVV388? Gotta investigate! Check out svv388211
Thank you for addressing this topic. It’s very relevant to me.
I found this very helpful and will be sharing it with my friends.
Gave jjwingame a shot, and it’s alright. Could use some improvements, but it’s got potential. Worth checking out at least once: jjwingame
jl10 casino https://www.jl10-casino.net
jiliokcc https://www.jiliokccw.com
ph789 login https://www.ph789-login.com
91phcom https://www.91phcom.net