Artificial intelligence in healthcare is used throughout the patient journey, from early detection and diagnosis through treatment, monitoring, and hospital operations.
This transformation is happening at a critical moment for health systems facing rising costs, workforce shortages, and ageing populations. Doctors and nurses are under pressure to do more with less, all while patients expect care that is not only safe and effective but also personalized, convenient, and on‑demand.
AI tools address this gap by automating routine tasks, surfacing the most urgent cases, and turning oceans of clinical data into insights that can improve outcomes.
In practical terms, that means algorithms helping radiologists catch cancers earlier, predictive models warning of complications before they escalate, and chatbots guiding patients between appointments with clear, accessible information. It also means smarter operating rooms, more efficient hospital operations, and remote monitoring that keeps people healthier at home rather than in a bed on the ward.
This article explores 10 of the most common and impactful applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare today, with a focus on real‑world use rather than distant promises.
What is Artificial Intelligence in healthcare?
Artificial intelligence in healthcare refers to computer systems that learn from medical data to support clinical decisions, automate tasks, and personalize patient care. These systems employ methods such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to analyze images, laboratory results, medical notes, and real‑time sensor data more quickly and often more consistently than humans.
At a Glance: Key Applications
| AI Application | Example Use Case | Key Benefit |
| Medical Imaging | Detecting cancer or stroke early | Faster, more accurate diagnosis |
| Predictive Analytics | Forecasting hospital readmissions | Early intervention and prevention |
| Personalized Medicine | Genomic-based treatment decisions | Better therapy outcomes |
| Drug Discovery | Screening molecules and drug targets | Accelerated R&D |
| Virtual Assistants | Chatbots and patient support | 24/7 assistance and engagement |
| Robotic Surgery | AI-assisted procedures | Greater precision and shorter recovery |
| Workflow Automation | Coding, scheduling, claims | Reduced admin workload |
| Remote Monitoring | Wearables for chronic care | Continuous health tracking |
| NLP for Clinical Data | Structured insights from notes | Improved documentation |
| Hospital Operations | Forecasting demand, managing inventory | Optimized resources |
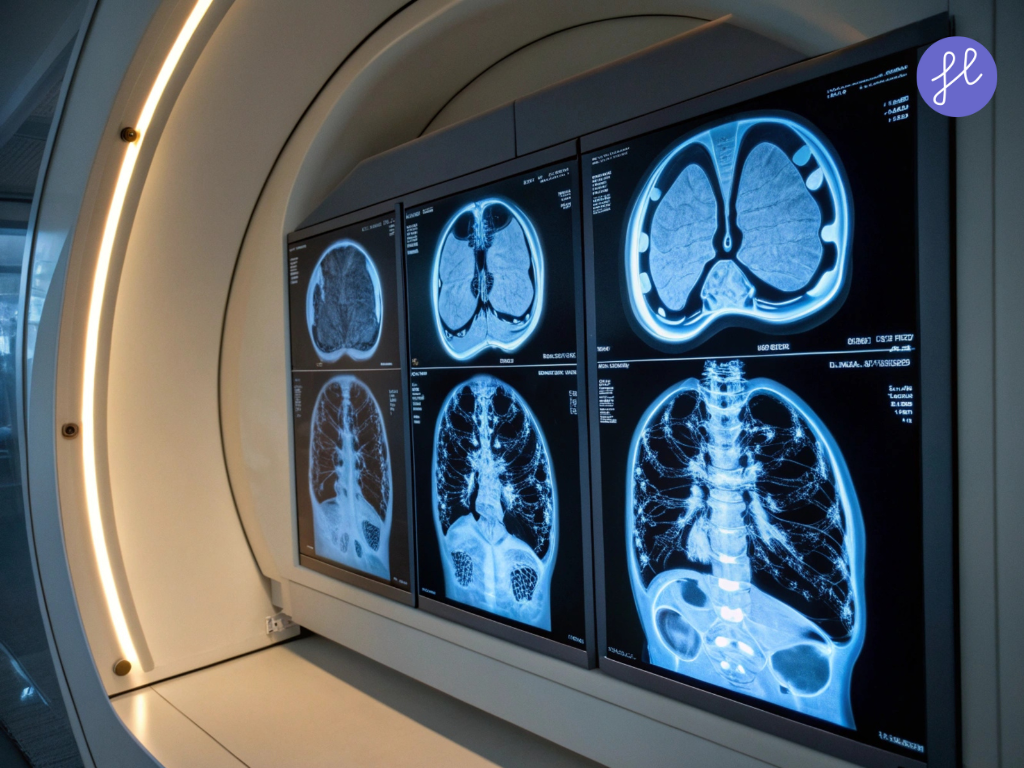
1. Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
One of the most common applications of AI in healthcare is medical imaging analysis for X‑rays, CT scans, MRIs, and mammograms. Algorithms can highlight suspicious lesions, fractures, or tumors and help radiologists detect diseases such as cancer, lung disease, and stroke earlier and more consistently.
Google Health’s AI system for breast cancer screening reduced both false positives and false negatives in tests published by Nature. Similarly, Lunit and Aidoc AI platforms help radiologists identify lung nodules or brain bleeds in real time.
Key benefits:
- Faster image reads and triage for time‑sensitive cases like stroke or trauma.
- Decision support that can reduce missed findings and support second opinions.
2. Predictive Analytics and Risk Scoring
AI models can predict which patients are at high risk of complications, readmissions, or disease progression by analyzing electronic health records, demographic data, and prior utilization patterns. These predictive tools support early intervention for conditions such as heart failure, sepsis, or diabetes complications.
Mount Sinai uses a deep learning model (“Deep Patient”) to predict heart failure well before symptoms appear. Cleveland Clinic applies predictive analytics to identify patients most at risk for postoperative infections.
Common use cases:
- Hospital readmission risk scores that trigger follow‑up calls or extra discharge support.
- Population health tools that identify patients who need screening or chronic care outreach.
3. Personalized and Precision Medicine
AI helps tailor treatments to the individual by combining clinical records, genetic data, and lifestyle information. In oncology and other complex fields, algorithms can analyze tumor genomics and recommend targeted therapies that are more likely to work for a specific patient.
Tempus and IBM Watson Health use AI to match cancer patients with targeted therapies based on tumor mutations and medical history.
Typical applications:
- Precision oncology treatment recommendations based on tumor mutations.
- Personalized dosing and therapy selection for complex conditions such as autoimmune disease.
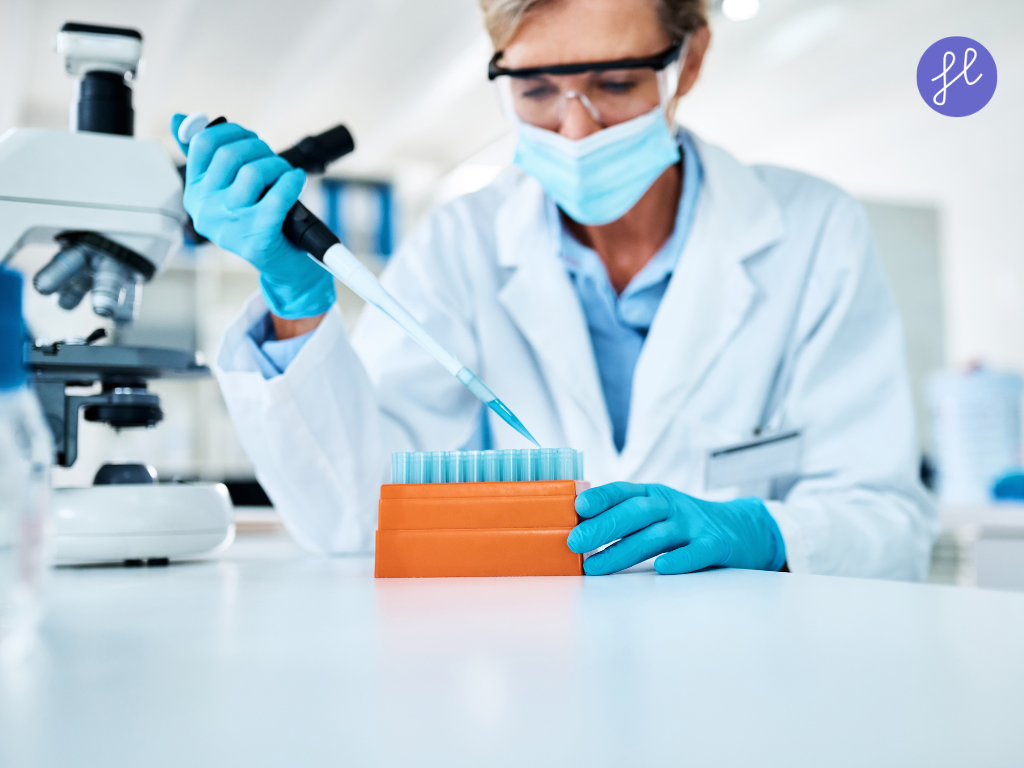

4. Drug Discovery and Clinical Research
Pharmaceutical companies use AI to screen large chemical libraries, model protein–drug interactions, and prioritize candidates more likely to succeed in clinical trials. This can shorten early discovery timelines and reduce the cost of bringing new therapies to market.
Insilico Medicine’s AI platform discovered a novel anti‑fibrosis drug candidate in under 18 months — a process that traditionally takes years. Pfizer and AstraZeneca use similar systems to prioritize compounds for trials.
Examples:
- Generative AI that proposes novel molecules matching desired biological targets.
- Algorithms that mine scientific literature and clinical data to find new indications for existing drugs.
5. Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots
AI‑powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 support for patients outside the clinic and communication-productivity support for healthcare professionals. They can answer common questions, triage symptoms, assist with scheduling, and send reminders about medications or follow‑up visits.
Babylon Health’s AI symptom checker guides patients on when to seek urgent care, while HosTalky is an all-in-one communication platform that improves healthcare professionals’ communication and productivity. Learn more about HosTalky’s top features.
Typical uses:
- Symptom checkers that guide patients on whether to seek urgent or routine care.
- Medication and appointment reminders are delivered through mobile apps or patient portals.
6. Robotic and AI‑assisted Surgery
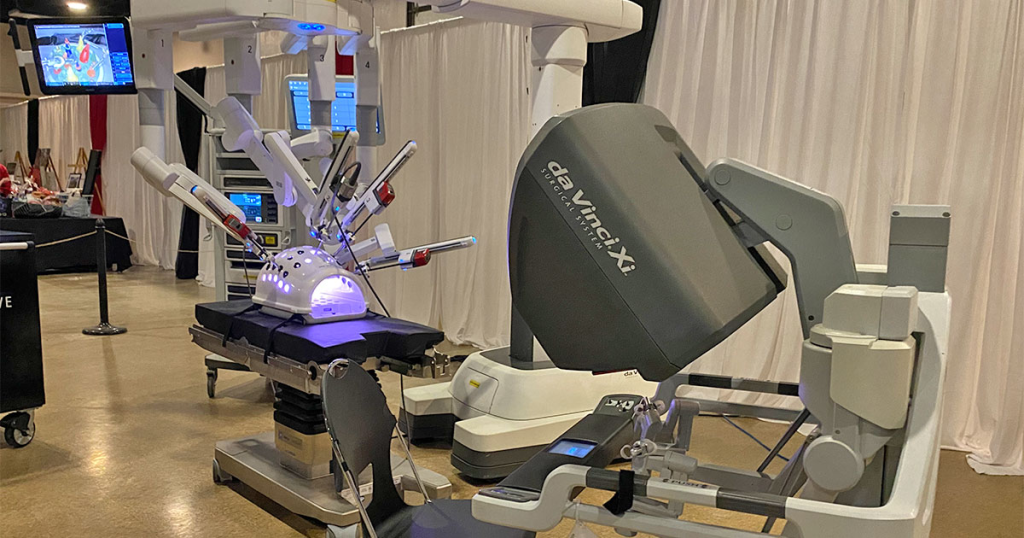
Robotic systems enhanced with AI can assist surgeons in performing minimally invasive procedures with higher precision and stability. These systems can filter tremors, suggest optimal cutting paths, and provide real‑time feedback based on imaging and sensors.
Benefits include:
- Smaller incisions, reduced blood loss, and shorter hospital stays for patients.
- More consistent performance in complex procedures such as neurosurgery or orthopedic surgery.
Intuitive Surgical’s da Vinci robot, guided by AI vision, has performed millions of minimally invasive surgeries globally. The Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins use AI systems to improve accuracy in brain and orthopedic surgeries.
7. Automated Clinical Workflows and Administration
AI tools automate routine administrative tasks, including coding and billing, documentation, and claims processing. By extracting information from clinical notes and forms, these systems reduce manual data entry and help staff focus on direct patient care.
Tools such as HosTalky AI Scribe and Nuance DAX integrate with Epic systems to automatically summarize clinician–patient conversations, converting them into structured EHR notes.
Common examples:
- Automatic assignment of diagnosis and procedure codes from clinical documentation.
- Intelligent scheduling and bed‑management systems that predict demand and optimize resources.
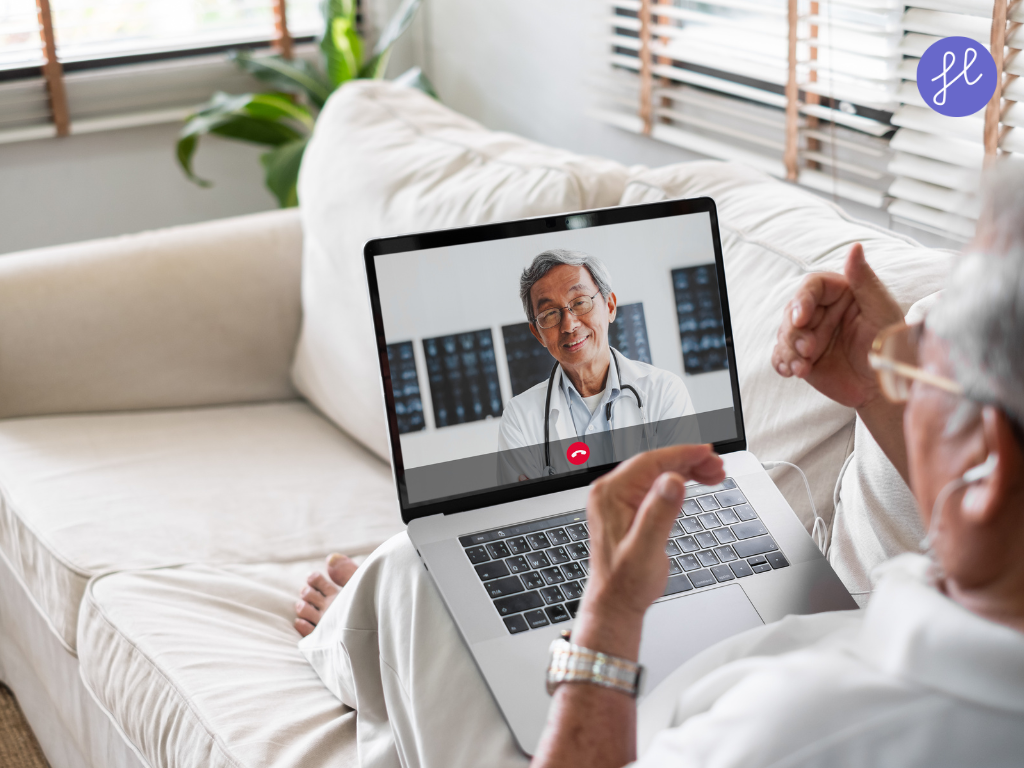

8. Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine
With connected devices and wearables, AI can continuously track vital signs and symptoms outside the hospital, flagging changes that require attention. Telehealth platforms increasingly incorporate AI to prioritize cases, summarize encounters, and support clinical decisions during virtual visits.
Biofourmis and Current Health platforms detect early signs of heart failure or COPD deterioration, alerting care teams before hospital admission is needed.
Use cases:
- Home monitoring of chronic conditions such as heart failure, COPD, and diabetes.
- Alerts clinicians when patterns suggest deterioration or medication non‑adherence.
Read more on Telehealth vs Telemedicine vs Telecare
9. Natural Language Processing for Clinical Data
Natural language processing (NLP) extracts structure and meaning from unstructured text such as progress notes, discharge summaries, and radiology reports. These tools can help build richer patient profiles, trigger clinical decision support, and improve information retrieval.
Examples:
- Automatic summarization of long medical records for faster clinician review
- Detection of key entities (diagnoses, medications, allergies) to support safety checks.
3M MModal’s ambient AI transcription captures clinical conversations in real time and automatically populates structured fields in EHR systems.
10. Hospital Operations and Resource Optimization
AI helps hospitals forecast patient volumes, optimize staffing, and manage supply chains. By learning from historical patterns and real‑time data, these systems can reduce bottlenecks, improve patient flow, and enhance the overall care experience.
Johns Hopkins Medicine’s Command Center uses AI dashboards to predict patient flow and anticipate bed demand, cutting emergency wait times by 20%.
Typical impacts:
- Predictive models for emergency department arrivals and inpatient bed demand.
- Inventory optimization for critical supplies and devices to reduce waste and shortages.
The Future of AI‑Enabled Healthcare

AI in healthcare is moving from research pilot to operational necessity. As hospitals and clinics adopt these tools, success depends on integrating them responsibly — ensuring transparency, patient privacy, and clinician oversight remain priorities.
The next frontier involves integrating all these applications—diagnostics, operations, and patient engagement—into a single intelligent ecosystem that continuously learns to deliver safer, more personalized care.
Fix the Disconnect. Streamline Every Shift.
HosTalky is the all‑in‑one, HIPAA‑compliant communication platform built for healthcare teams. It eliminates missed messages, data silos, and compliance headaches while helping every care team stay connected—anytime, anywhere.
What you can do with HosTalky:
- AI Scribe – Convert clinical conversations into structured notes in seconds.
- Medigenie – Summarize complex charts and draft consult requests with AI precision.
- Meditionary – Get quick definitions for any medical term without breaking workflow.
- &CareID – Your portable professional ID. Connect securely across facilities.
- Priority Reminders & Tasks – Assign, track, and complete follow‑ups seamlessly.
- Secure Chats & Groups – Collaborate instantly with clinical peers or entire teams.
- Broadcast Alerts – Share critical updates hospital‑wide, visible and actionable.
Stay compliant. Stay connected. Stay focused on patient care.